Why is thumb sucking bad?
From birth, children have used sucking actions to calm themselves. In reality, many parents rely on pacifiers, teething toys, and other suckable things to help their infants control their emotions.
As youngsters get older, they may become accustomed of sucking their fingers or thumbs. Admittedly, thumb sucking can have long-term detrimental implications if performed after the age of four. The following are five potential negative effects of thumb sucking.
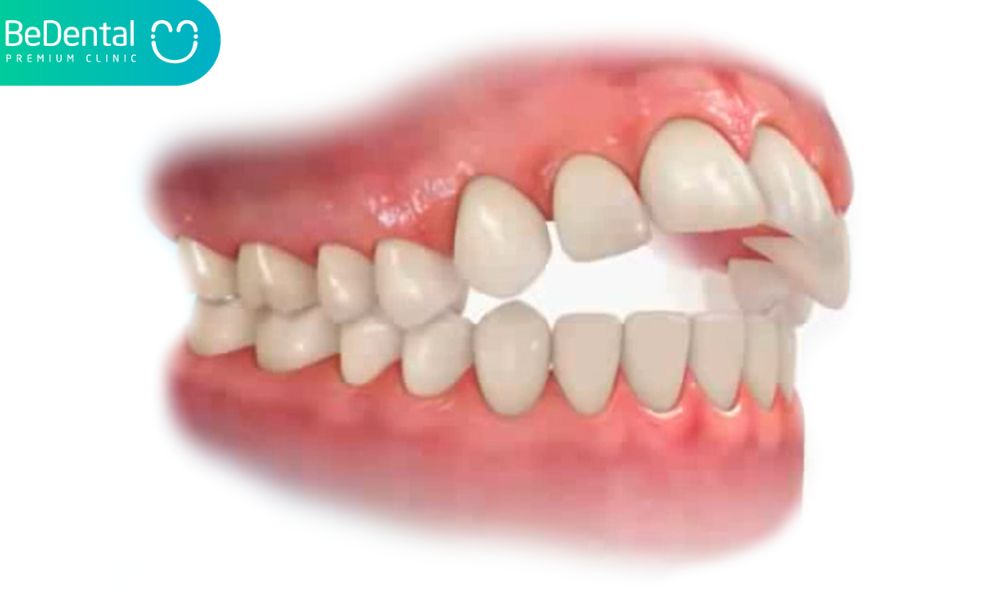
5 side effects: Open Bite
The most significant long-term effects of thumb sucking are various forms of dental malocclusion. Malocclusion is a word used to describe noticeable tooth misalignment while the mouth is closed. The next section will discuss two of the most frequent malocclusions induced by thumb sucking: open bite and overbite.
The bite becomes open when the top and bottom front teeth are directed outward. Even when your child’s mouth is entirely closed, the front teeth do not make contact due to this misalignment.
Open bite may need future orthodontic treatment or aggravate other tooth misalignments that require orthodontic treatment.
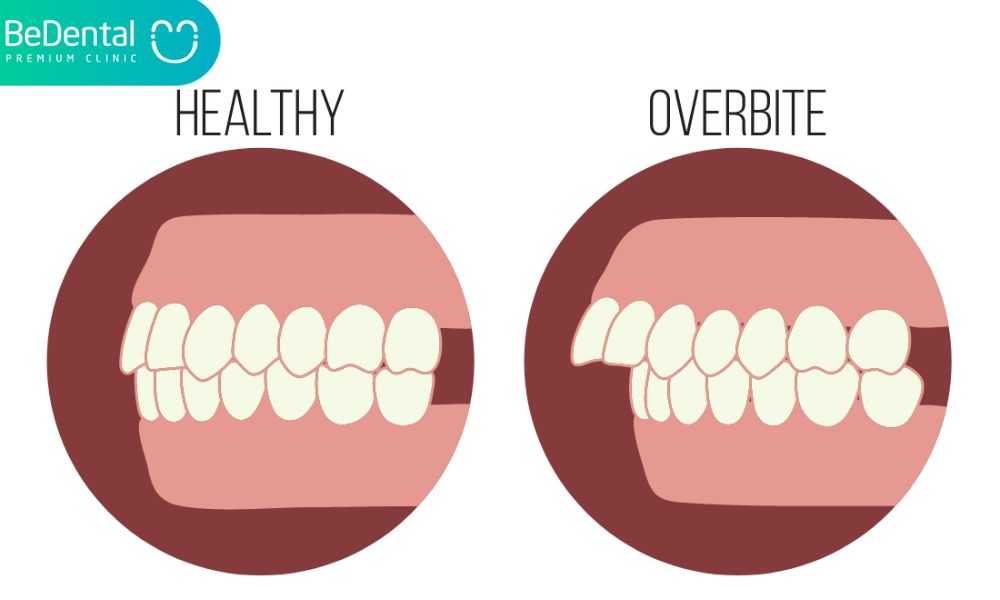
5 side effects: Overbite
Overbite occurs when the teeth get pointed outward, similar to open bite malocclusion. With an overbite arrangement, however, this misalignment is limited to the top front teeth. As your child closes his or her mouth, the top teeth cover the bottom teeth instead of the top and bottom teeth regularly touching.
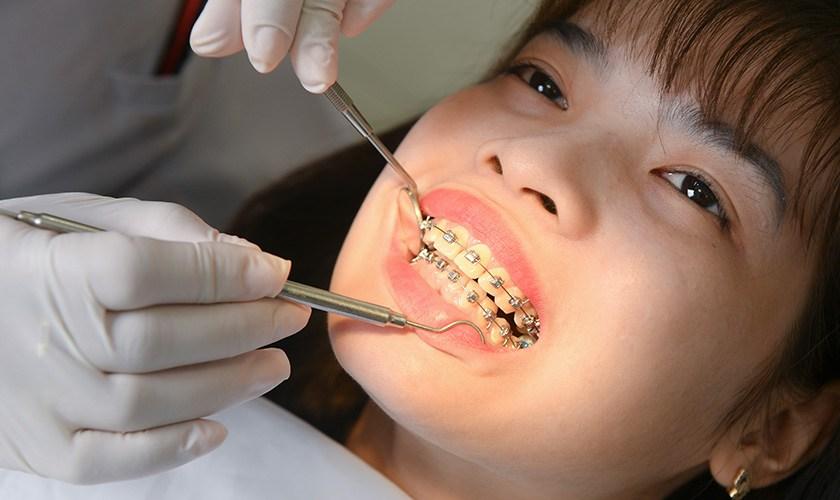
Overbite malocclusion can alter the contour of the face and grin. To rectify severe overbites, significant orthodontic treatment may be required.
Since overlapping teeth can make typical metal braces bracket placement difficult, individuals with overbites may require treatment with headgear and other alternative orthodontic equipment in some situations.
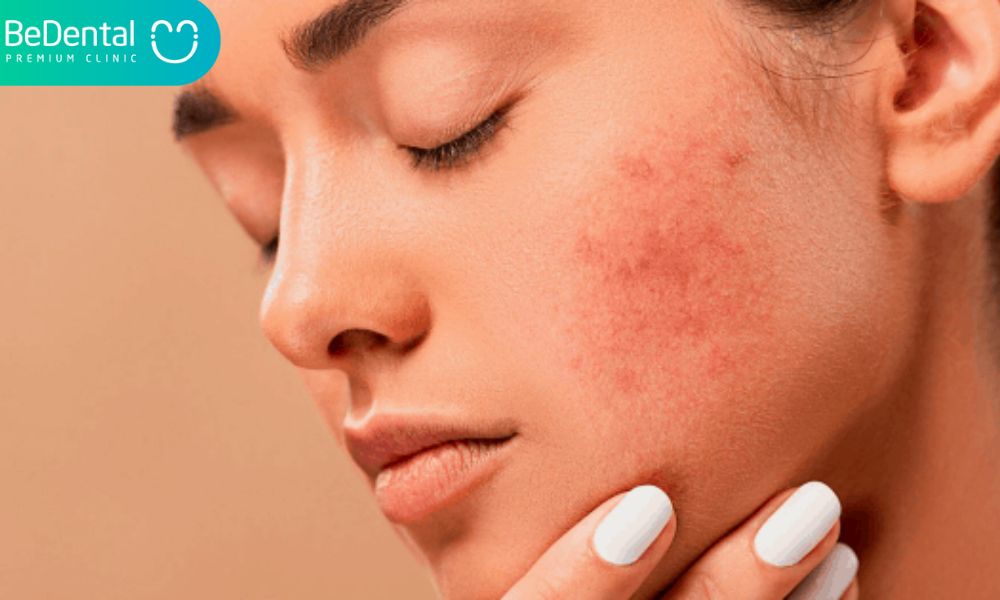
5 side effects: Skin Problems
Long-term thumb sucking in children can cause uncomfortable or severe skin issues on their favored thumb. When the skin is exposed to the moisture of the mouth, it becomes more prone to injury. The skin may break or bleed in rare situations, leaving your child’s hands prone to infection.
The thumb may develop callosities. The pressure and dampness of thumb sucking may potentially deform the thumbnail, producing ingrowth or peeling.
If your child’s thumb sucking creates significant skin issues, you may need to discourage the activity by bandaging the damaged thumb, wrapping it in a medical finger glove, or otherwise covering the thumb. Aversion strategies, such as putting your finger in an unpleasant-tasting substance, should be avoided since they can be very frustrating and seldom generate long-term outcomes.
5 side effects: Speech Impediment
Since it impacts the development of the teeth, jaw, and palate, thumb sucking can alter how your child eats and communicates. Lisping and other speech impairments can occur from thumb sucking, such as difficulties pronouncing harsh consonant sounds like “D” and “T.”
Because distorted sounds are created in part by the structure of your child’s teeth in relation to his or her tongue, even high-quality speech therapy may not totally repair these difficulties without adequate dental care.
Your child’s ability to communicate successfully may be hampered by speech impairments. Many children with speech impairments suffer feelings of frustration, rage, and isolation.
5 side effects: Social Issues
Even if your child’s thumb sucking does not endanger his or her dental development, the behavior may cause social issues. Youngsters who suck their thumbs in public may face ridicule from their classmates. While thumb sucking is a typical childhood practice, people may condemn him or her for maintaining the activity as your child grows older.
Thumb sucking is an unconscious response to stress or boredom for many children. Because your child may not consider before putting his or her thumb to work, he or she may want your aid and education to stop the habit within the proper developmental time.
When you strive to assist your kid quit thumb sucking, keep in mind that it does not signify any physiological or developmental problems. Your youngster may need your help, as well as the help of a dentist or doctor, to break the habit. Yet, eradicating thumb sucking behavior is a long-term aim that should be done through positive reinforcement rather than punishment.
In children without permanent teeth, thumb sucking is typically harmless. Yet, when your child’s baby teeth fall out and adult teeth appear, you should urge him or her to seek alternative types of comfort.
More
Tongue Scrapers: 7 benefits you should know
Teeth cleaning for children at home: How to Clean Your Child’s Teeth
Tooth decay and 11 risk factors
Tartar and 6 ways to prevent its return
Toothache and 6 common symptoms







Pingback: Oral health: An overview to your oral health – Be Dental
Pingback: Teeth fluorosis: 4+ things you must know – Be Dental
Pingback: Thumb sucking: 5 side effects of thumb sucking | Nha Khoa Bedental