Periodontal disease is inflammation and infection of your gums and the bone that supports your teeth. It can be a result of poor hygiene, but some people are more prone to this type of infection. Symptoms may include bad breath, loose teeth and bleeding, swollen gums. There are many treatments available, depending on the severity of disease.
Definition of periodontal disease
Infections and inflammation of the gums and bone that surround and support the teeth are the major causes of periodontal diseases. The gums might swell up, get red, and even bleed in the early stages of gingivitis. In a more severe form, known as periodontitis, the gums may peel away from the tooth, which can potentially result in bone loss, tooth loosening, or even tooth loss. Most cases of periodontal disease occur in adulthood. The two main dangers to oral health are periodontal disease and tooth decay.
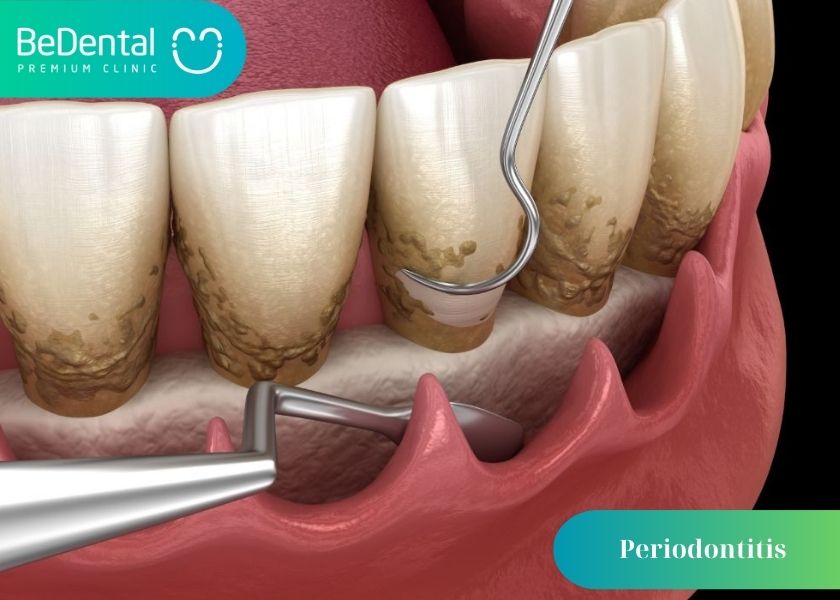
Causes of periodontal disease
Bacteria in the mouth infect the gum tissue surrounding the tooth, resulting in inflammation and periodontal disease. Plaque, also known as calculus, is created when germs remain on the teeth for an extended period of time. The teeth are harder to clean when tartar builds up below the gum line. Only tartar removal by a dental professional will halt the progression of periodontal disease.
Symptoms
Periodontal disease is anticipated by the warning signals listed below:
- A persistent unpleasant taste or bad breath
- Gums with red or swelling
- Bleeding or sensitive gums
- Struggle with chewing
- Missing teeth
- Sensitive teeth
- Your teeth’s gums having separated
- Any modification to the way your teeth bite together
- Any modification to the partial dentures‘ fit
Risk factors
Periodontal disease is risky because of a few things:
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Oral hygiene issues
- Plaque and tartar
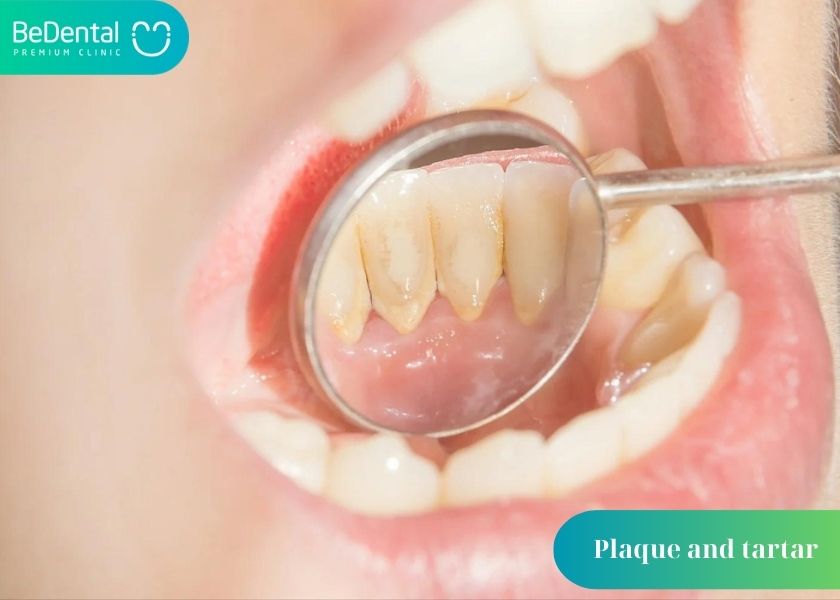
- Stress
- Heredity
- Uneven teeth
- Immune deficits that are underlying, like AIDS
- Placings that have degenerated into defects
- Taking medicine that makes you feel dry mouthed
- Old bridges that don’t fit anymore
- Alterations in female hormones brought on by pregnancy or the use of oral contraception
Prevention
Following these steps can help prevent or manage periodontal diseases:
- Brush and floss every day to remove the bacteria that cause gum disease.
- For checkups, see the dentist at least once a year, or more frequently if you have any of the risk factors or warning symptoms listed above.
Treatment
A healthy mouth and frequent professional cleanings help prevent and treat periodontal disease. Although more intensive care may be needed, more severe cases of periodontal disease can still be effectively cured. Deep cleaning of the tooth root surfaces below the gum line, oral prescription drugs, topical treatments applied directly to the gums, and occasionally corrective surgery may all be part of this type of therapy.
12 common periodontal diseases
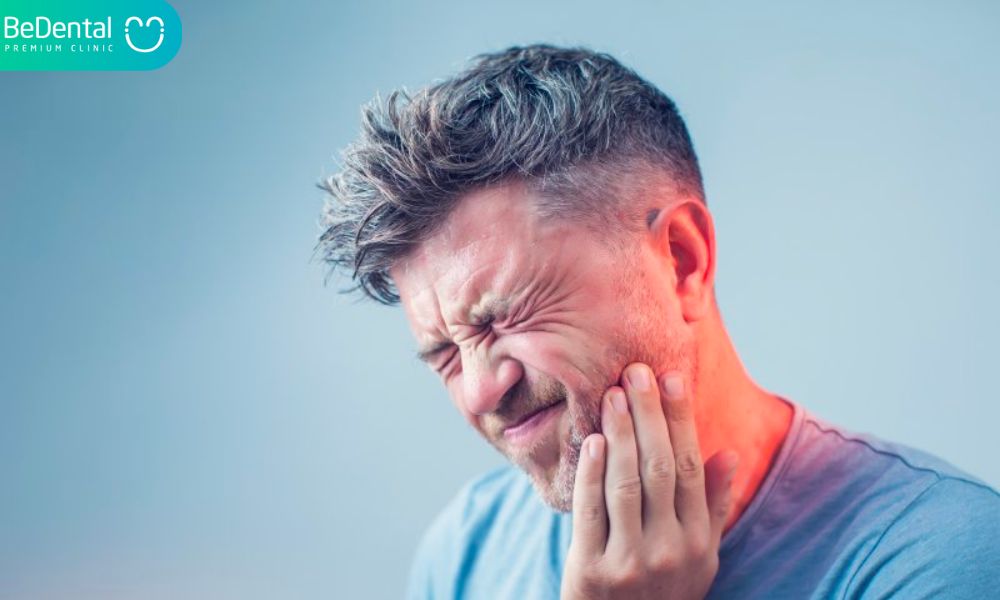

A toothache refers to pain in or around the teeth and jaw that’s usually caused by tooth decay. Mild toothaches are caused by temporary gum irritation that you can handle yourself. However, more severe toothaches come from dental diseases that won’t get better on their own and will need to visit the dentist.
- Stained Teeth
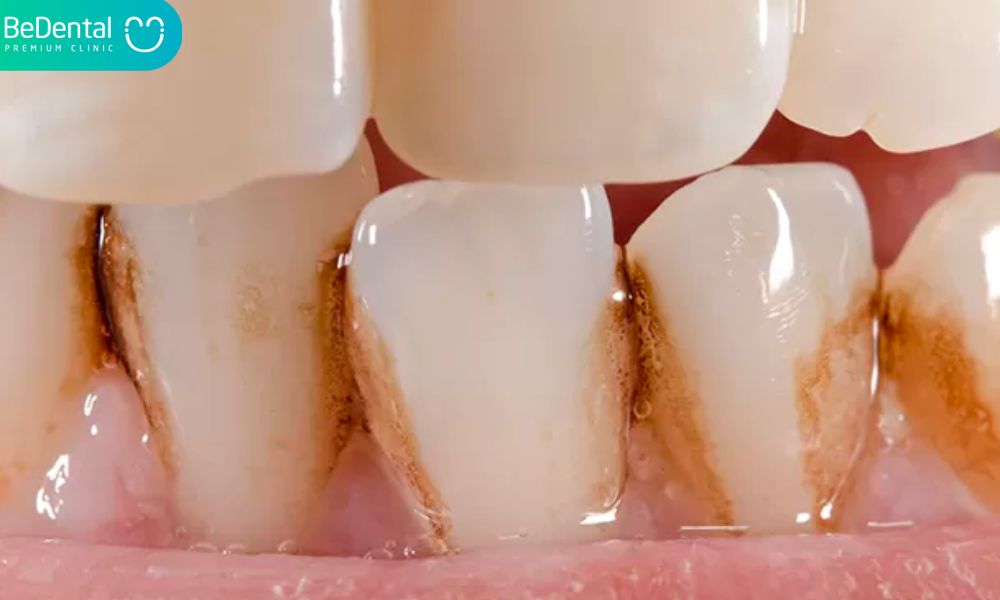
The proper method will be able to remove numerous stains from your teeth, much like your laundry. Your teeth may become discolored due to trauma, drugs, cigarettes, and certain foods. For lightening them, you have three possibilities. In addition to a particular light, your dentist may use a whitening product. Or you might bleach them at home using a plastic tray and gel purchased from a shop or your dentist. Whitening toothpaste and rinses are the easiest option, but they only remove superficial stains.
It’s unfortunate that you have these tiny gaps in your teeth. You develop them when a layer of sticky bacteria on your teeth known as plaque accumulates and begins to progressively erode the enamel, the tooth’s strong outer coating. Along the gum line and on the margins of prior fillings, adults might also experience tooth decay issues. Reduce your intake of sugary snacks, floss every day, use fluoride mouthwash, brush your teeth at least twice a day, and attend your dentist check ups regularly to help avoid tooth decay. If a sealant would be helpful for you, ask your dentist.
It’s the most common kind of dental damage. Accidents can result in chips. Similarly, doing something far less dramatic, like eating popcorn, can. If the chip is significant, your dentist could advise a crown or bonding using a strong resin substance to repair the damaged region. If the pulp is in danger, you could require a root canal, then a veneer or crown.
- Impacted Teeth

“Impacted” refers to an adult tooth that doesn’t emerge normally. It often occurs when a tooth is damaged on soft tissue, bone, or another tooth. A dentist could advise not worrying about it if you don’t find it unpleasant. But an oral surgeon can remove it if it hurts or could lead to issues in the future.
- Cracked Tooth
You may not know how it happened, or perhaps you were chewing while playing football without a mouthguard, but you now have a fractured tooth. Can the tooth be saved by your dentist? It varies. Most dentists recommend crowns for teeth with cracks to prevent the crack from growing worse. The problem becomes more difficult if the tooth is both heat- and cold-sensitive. Until you visit the dentist, try to chew on the opposite side. You could require a root canal and a crown if the break extends past the gum line. However, if the break is more severe, the tooth must be removed. Fillings may make cracks more likely to occur.
When ice cream reaches your teeth, it shouldn’t hurt, it should taste delicious. Determine the reason as a first step. Cavities, damaged dental enamel or fillings, gum disease, broken teeth, or exposed roots are just a few possible causes. After determining the condition, your dentist may recommend a filling, a root canal, or gum treatment to restore tissue lost at the root. Instead, you could require a fluoride gel, desensitizing toothpaste, or a strip.
- Too Many Teeth (Hyperdontia)
How many teeth do you have? You should have had 20 “baby” teeth, and you now have 32 adult teeth. Hyperdontia, or having additional teeth, is a somewhat uncommon condition. People who have it may also have Gardner’s Syndrome or a cleft palate. The additional teeth must be extracted, and the bite must be adjusted using orthodontics.
- Crooked Teeth

Orthodontics, the solution, is not just for children. Additionally, correcting your bite and straightening your teeth doesn’t merely result in a nice smile. By easing symptoms like jaw discomfort, it can be a significant contributor to enhancing overall oral health. Orthodontists may use retainers, aligners, and braces (metal or ceramic).
- Gap Between Teeth
You might not think much of a gap between the front teeth. But if you want to fix it, you have aesthetic alternatives like veneers or bonding as well as orthodontics to shift your teeth closer together.
- Wisdom Teeth Problems
Consider yourself lucky if your dentist reports that your wisdom teeth or third molars arrived without any issues. 90% of people have at least one wisdom tooth that is partially or completely impacted. Cavities, harm to adjacent teeth, and gum disease can all be brought on by issues with your wisdom teeth. Typically, wisdom teeth grow between the ages of 17 and 25. Your dentist should check up on their development. It could be necessary to have them removed if they start to cause issues.
- No Room to Floss
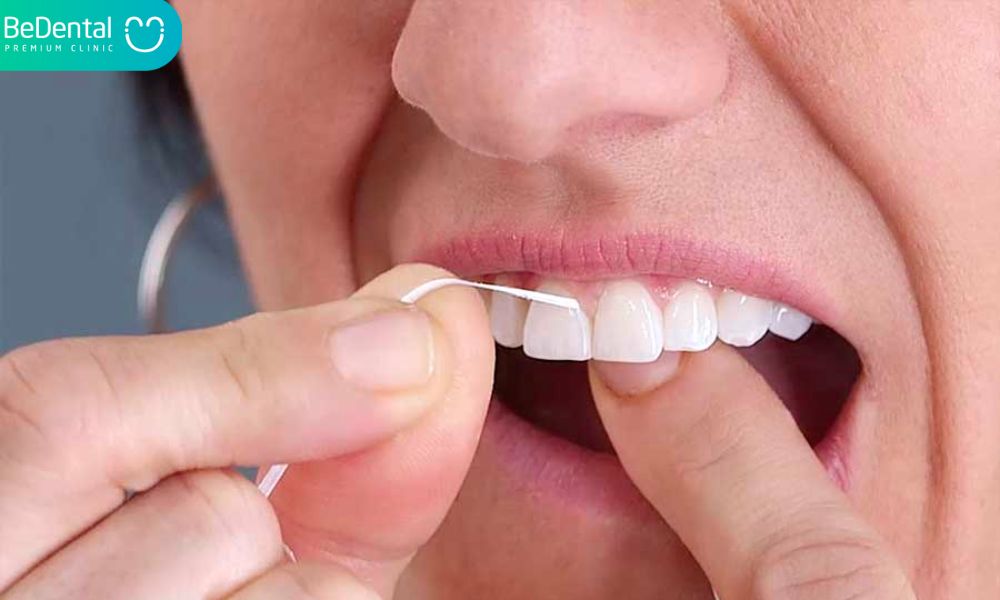
Always leave space between your teeth for floss, no matter how snug the fit. In such a case, you might have to convert to waxed or a thinner floss. Additionally, you may experiment with other tools, such a toothpick or a looped flosser. Use a product that works for you after some trial and error, and then use it consistently after that. Good dental health requires daily flossing.
Q&A
What are the periodontal diseases of the tooth?
Cavities (tooth decay), gum disease (periodontitis), and oral cancer are some of the most frequent periodontal diseases that affect our oral health. In the last year, more than 40% of individuals reported experiencing oral discomfort, and by the time they are 34, more than 80% of people will have experienced at least one cavity.
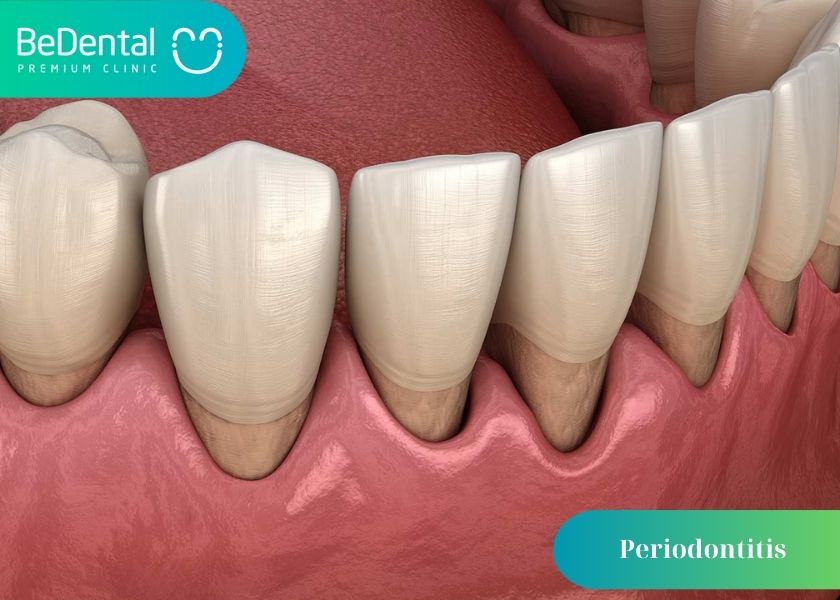
What is one of the most common periodontal disease?
Tooth decay, which affects millions of children and adults worldwide, is one of the most prevalent periodontal disease. When you don’t clean your teeth after ingesting a lot of sugary and acidic meals and beverages, you risk developing cavities. Cavities are the outcome of tooth decay.
What does the most damage to your teeth?
The worst thing you can do to your teeth is eat candy.
Since they are high in sugar, it is more difficult for saliva and water to wash them off of your teeth. To protect your teeth, just consume candy and snack items in moderation.
What foods clean your teeth?
There are certain specific foods that can help clean your teeth and mouth, but a balanced diet is crucial for both dental and general health:
- Carrots.
- Apples.
- Celery sticks.
- Popcorn.
- Cucumbers.
- Pears.
- Lettuce.
- Cheese.
See more
Gum Disease and 3 Factors to Recognize Gum Disease
Bad Breath and 6 Common Questions
How to Handle 3 Types Of Dental Emergencies While Working Abroad
Tooth Fillings and 3 Problems with Tooth Fillings
Tooth decay and 11 risk factors
Tư vấn chuyên môn bài viết:
BÁC SĨ DƯƠNG THỊ THÙY NGA





Pingback: Periodontal disease and 12 common periodontal diseases | Nha Khoa Bedental
Pingback: Tooth extraction and 4 noticeable questions need to know – Be Dental
Pingback: Teeth cleaning and 3 main concerns – Be Dental