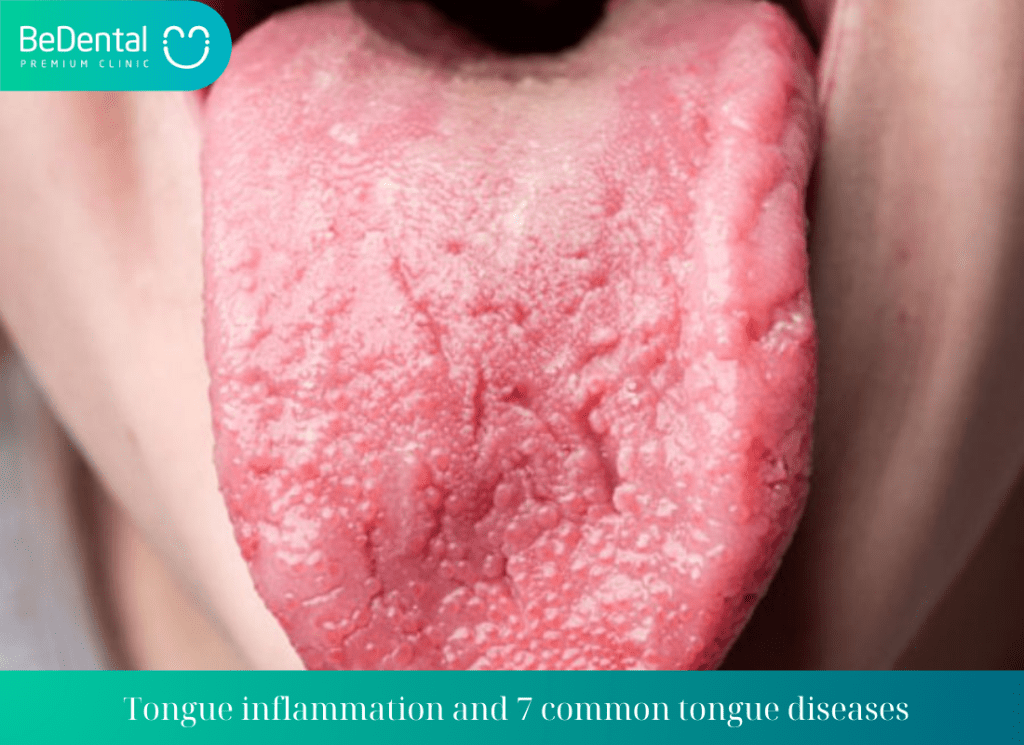
Tongue inflammation and 7 common tongue diseases. is a fairly common condition that causes your tongue to swell, change color, and exhibit unusual symptoms. The taste buds on the surface of the tongue, which contain thousands of taste receptors that help you perceive food, can also be affected in cases of severe tongue inflammation.
If you are experiencing tongue inflammation, you may need to modify your eating and speaking habits to minimize the pain, swelling, and redness of the tongue. Let’s learn more about this condition and the solutions to alleviate discomfort from tongue inflammation.
Tongue inflammation and 7 common tongue diseases
Tongue inflammation can be a typical disease of the tongue caused by infection, allergies, or sensitivities. It can also be a symptom of another condition such as vitamin deficiency, primarily B-group vitamins, niacin deficiency, congenital anemia, or zinc deficiency. It can be associated with systemic skin disorders such as peeling, psoriasis, eczema, or cancer, etc.
Common symptoms include redness, severe swelling, water blisters, cracks or fissures on the tongue, ulcers or erythema, dryness, smoothness, with or without coating.
- Tongue inflammation can be classified into three types:
- Acute tongue inflammation: Tongue inflammation that appears suddenly along with other symptoms.
- Chronic tongue inflammation: Tongue inflammation that recurs multiple times.
- Hunter’s glossitis (glossitis with necrosis): The condition develops when multiple taste buds disappear, and the tongue undergoes changes in both color and structure.
The treatment of tongue inflammation should be carried out under the guidance of a doctor. Antibiotics should be used in case of bacterial infection, antiviral drugs if there is a viral infection, antifungal medication if the inflammation is caused by a fungus, and vitamin supplements if the inflammation is due to a vitamin deficiency.
Additionally, patients should take careful oral hygiene measures and avoid consuming hot and spicy substances such as alcohol.
See more: What is white tongue disease
See more: The 10 most common oral diseases, causes and treatment directions.
Tongue migratory glossitis
This is a condition where the surface of the tongue changes color, the top layer of tongue skin is never replaced, or the tongue skin is peeled off too early, exposing a red area resembling scratches on the skin, leading to tongue pain. Other causes may include a family history or tongue injury.
Individuals with acute tongue inflammation will experience red, ulcer-like areas with a pale yellow border, typically on the dorsal surface of the tongue, but they can also appear on the anterior body of the tongue or the floor of the mouth.
Although migratory glossitis is not serious and often resolves on its own, it can cause significant discomfort for those affected. Symptom management can be achieved by regular mouth rinsing and meticulous oral care.
To prevent migratory glossitis, it is important to:
- Avoid consuming spicy, bitter, or acidic foods
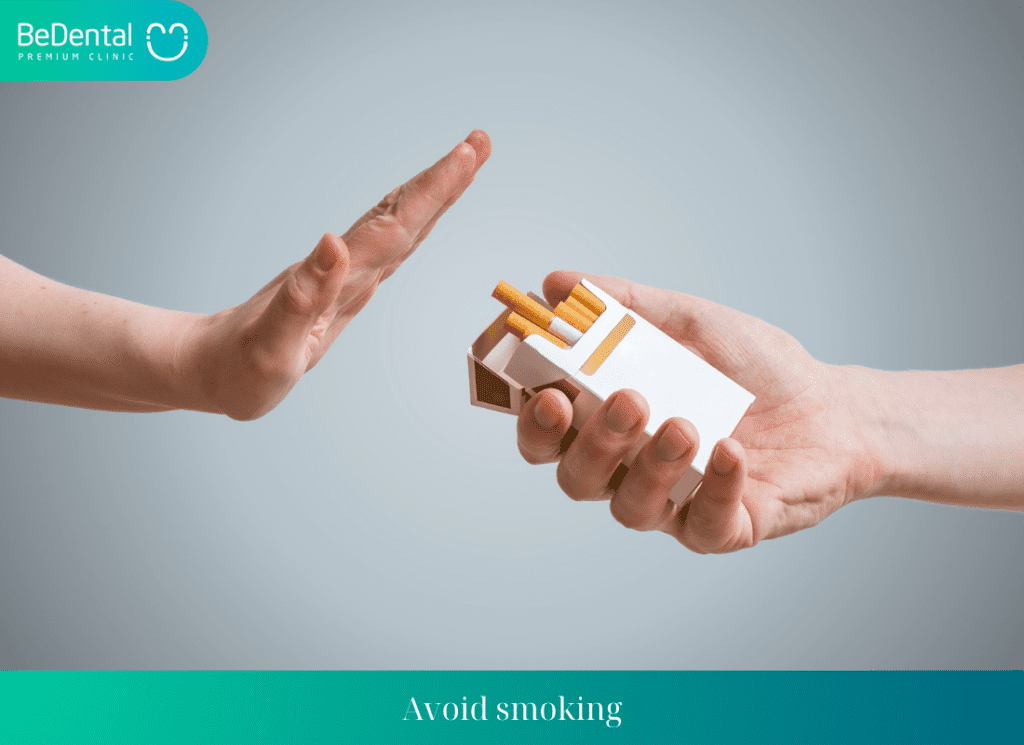
- Avoid smoking
- Avoid using toothpaste with strong chemicals or tooth whitening properties.

See more: Tetracycline antibiotic ointment for skin. 5 Tetracycline side effects
Geographic tongue
Geographic tongue is a common and frequently encountered condition. The circular patches on the surface of the tongue give it the appearance of a map. However, this condition can also cause some discomforting symptoms such as decreased taste sensation and difficulty in eating and drinking.
Fortunately, geographic tongue is often a mild condition and can be treated with anti-inflammatory and analgesic medications or systemic medications as prescribed by a doctor, combined with regular oral care. Additionally, patients should limit the consumption of spicy, acidic foods, and carbonated beverages to minimize uncomfortable symptoms.
Apthous ulcers
Apthous ulcers, also known as mouth ulcers, are a condition where multiple ulcers appear on the underside or top of the tongue, causing the patient to feel sore and painful, affecting their ability to swallow and speak. Recurrent ulcers can lead to weight loss, fatigue, and a decreased quality of life.
5 effective ways to fix deviated faces. What should I do if my face is skewed left or right?
Apthous ulcers can be classified into three types based on the size, location, and duration of the ulcers:
- Minor apthous ulcers: Few ulcers, each measuring less than 5mm, heal within 7-10 days without leaving any marks.
- Major apthous ulcers: One or more ulcers, each measuring 1-3 cm, lasting up to 6 weeks, and may leave scars upon healing.
- Herpetiform ulcers: Typically 10-100 ulcers, each measuring 1-3 mm, mild in nature, and heal within 7 days.
Other factors that contribute to the development of apthous ulcers include environmental factors, mechanical trauma, alcohol use, anemia, metabolic disorders, and stress.
Patients with this condition should follow the treatment protocol prescribed by their doctor, which may involve medication or systemic treatment. It is also recommended to undergo necessary tests to check for any underlying anemia or other conditions.
White tongue
White tongue is a condition where the tongue appears pale instead of its usual pink color and has white spots on its surface due to bacterial infection. White tongue is often caused by poor oral hygiene habits, dry mouth, oral thrush, frequent tobacco use, and alcohol abuse.
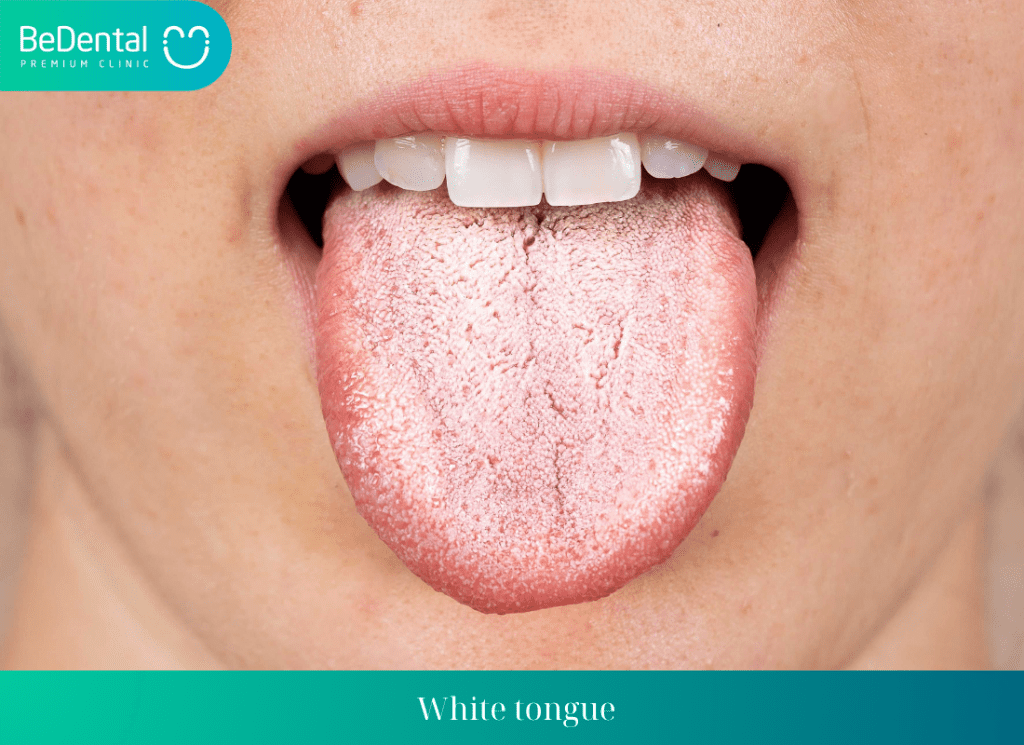
Remedying white tongue is relatively easy by maintaining regular oral hygiene, thoroughly cleaning the tongue, using filtered water, and using mouthwash to freshen breath.
Additionally, patients should gargle and rinse the mouth and throat regularly with a mixture of honey and a small amount of fresh turmeric to help restore the mucous membranes of the nose and mouth quickly.
See more: What is dumpling cheeks? 5 simple ways to own dumpling cheeks
Leukoplakia
Leukoplakia is a form of oral lesion that tends to be hereditary. It presents as homogeneous white patches on the tongue and oral mucosa, whether it is benign or malignant. Due to the inability to subjectively determine the severity of the condition, patients need to undergo tests to accurately assess the extent of the disease.
The exact cause of leukoplakia is not yet clearly determined, but the risk of developing the disease is increased by factors such as smoking, excessive use of stimulants, and alcohol consumption.
The following measures can be taken in the treatment of leukoplakia:
- Benign condition: The ulcers will heal on their own, and there is no specific treatment. It is important to eliminate any risk factors that may cause cancer.
- Malignant condition: If the test results confirm the presence of stomach cancer, it is necessary to remove the ulcer to prevent the spread of cancer.
Prevention of leukoplakia can be achieved by avoiding tobacco use, abstaining from alcohol consumption, and incorporating fresh vegetables and fruits into the diet.
Tongue cancer
The most common type is squamous cell carcinoma, which is seen in both the lips and tongue. Sometimes, cancer can appear as leukoplakia before it develops, or it may have no clear signs.
The first symptom to suspect the disease is the appearance of a long-lasting ulcer with a white or red color on the front surface of the tongue, causing pain. Other accompanying symptoms may include:
- Jaw pain and throat itching
- Pain while chewing
- Difficulty in chewing due to an obstruction in the teeth
- Sore throat or jaw
- Difficulty in chewing and swallowing food
- Tongue bleeding without cause
- Persistent lump on the tongue
- Currently, the direct cause of tongue cancer has not been identified, but it has been linked to certain risk factors such as:
- Smoking and alcohol consumption
- Poor diet lacking fruits and vegetables
- Infection with human papillomavirus (HPV) in children
- Family history of tongue cancer
- Previous history of cancer
The treatment of oral cancer involves surgical removal of cancerous cells, and the complexity of the surgery depends on the size of the tumor. Along with surgery, patients may also require chemotherapy or radiation therapy to eliminate any remaining cancer cells
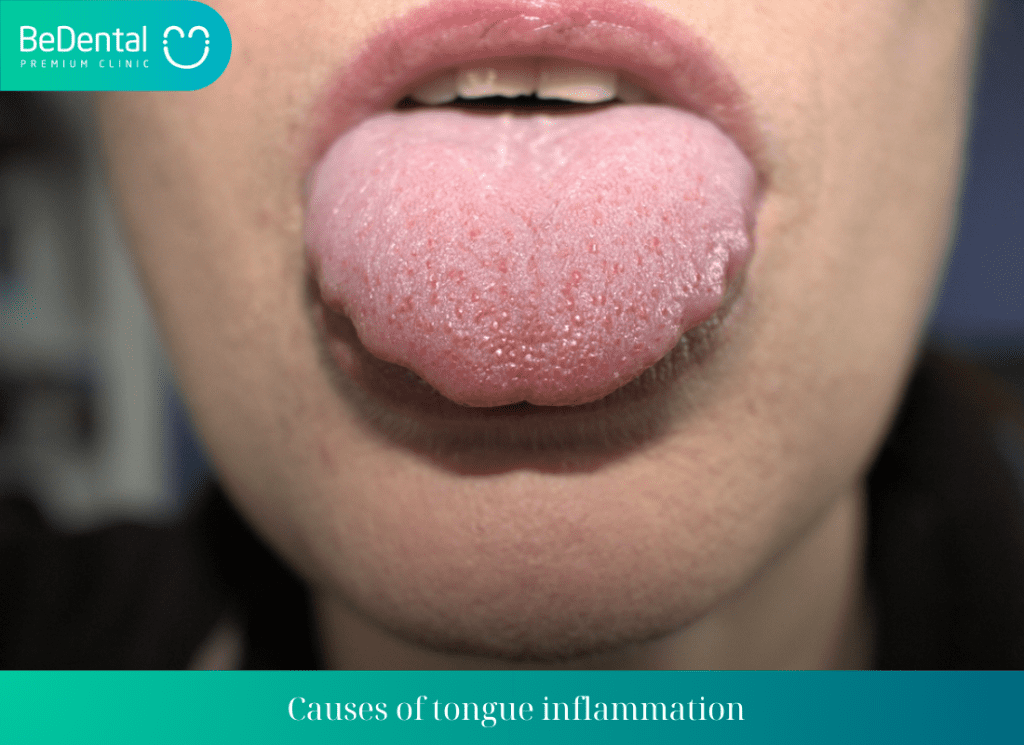
Causes of tongue inflammation
There are several causes of tongue inflammation, and below are some common ones:
- Allergens: Exposure to allergens such as medications or foods can cause tongue inflammation and other related symptoms. Early intervention is important to prevent risks for the patient.
- Viral infection: A common cause of tongue inflammation is viral infection. Various types of viruses can attack the tongue, weaken the immune system, and affect the taste buds and tongue muscles. For example, the Herpes simplex virus often causes tongue pain, swelling, and blisters around the mouth.
- Iron deficiency: Tongue inflammation can also be a sign of iron deficiency. Iron is an essential element for red blood cell production and myoglobin, which plays a crucial role in tongue muscle structure. Iron deficiency can contribute to tongue inflammation.
- Oral trauma: Strong impacts or injuries to the oral region can create favorable conditions for bacterial attack and result in tongue inflammation.
Characteristic signs of tongue inflammation
What are the characteristic signs of tongue inflammation? If you experience the following unusual symptoms on your tongue, there is a high likelihood that you have tongue inflammation:
- Swollen and painful tongue.
- Cracks or fissures on the surface of the tongue.
- Changes in the color of the tongue.
- Persistent itching or irritation of the tongue.
- Difficulty in basic activities such as eating and speaking.
- Loss of taste buds, resulting in a loss of the ability to taste food.
- Increased sensitivity of the tongue when inflamed.
Subjective changes in the characteristic signs of tongue inflammation should not be ignored, especially if they are prolonged, recurring frequently, and accompanied by symptoms such as bleeding, tongue soreness, throat and jaw pain, and difficulty swallowing.
Experts advise not to overlook any characteristic signs of tongue inflammation, no matter how small. It is important to seek early medical examination for diagnosis and timely treatment, reducing the risk of complications.