What Are Molars in Vietnam? Is There Any Replacement? When it comes to molars, we are often warned that they are extremely important teeth. However, not everyone understands exactly what molars are. The article below will help you learn about what premolars and molars are.
What are molars in Vietnam?
What are molars in Vietnam? What is a molar is always a concept that many people are interested in. Because many people know that they are very important but do not define exactly which teeth are molars.
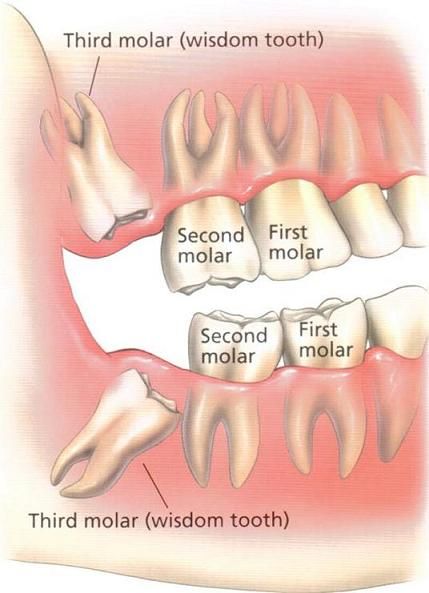
So what are molars in Vietnam? Molars are also known as molars. These are the teeth that grow on the inside of the jaw. It protects the jawbone and is responsible for chewing.
Molars are located within two incisors and one canine tooth. Each quadrant of the jaw will have two premolars and four large molars.
Quantity
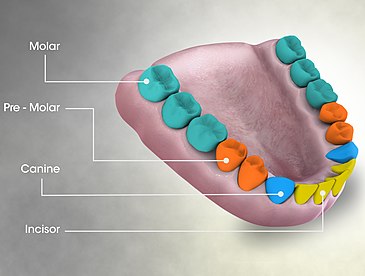
When learning about molars, you need to understand the number of molars. An adult usually has 12 molars. 6 on top and 6 on bottom. Each side of the upper and lower jaw will have 3 molars.
They occupy the posterior part of each hemiarch. In addition, this is a group of teeth that do not grow to replace baby teeth, they are called successor teeth.
See more: AFTER SCALING WHAT ARE THE CAUSES OF TEETH SENSITIVITY ?
Time of molar eruption
First molars usually erupt when we are about 6 years old. This is the first permanent tooth to grow in the oral cavity. The second molars will erupt when we are about 12 years old. The third molars are often called wisdom teeth and they grow at different times depending on each person’s constitution.
Function
Large molars are responsible for chewing and crushing food. At the same time, it also maintains the vertical dimension of the floor below the surface. The position of the teeth relative to the temporomandibular joint will help the teeth have the best grinding function.
Shape of molars
The most recognizable characteristics of molars are:
- They are called molars because they have the largest chewing surface on the dental arch.
- Each molar usually has 3 – 5 large cusps.
- This is the only group of teeth where each tooth has at least 2 outer cusps.
- There are two or three large roots, and the position and direction of the roots are most characteristic of the group.
- The chewing surfaces of molars are quite cusped with solid roots.
Below is a table of size and age of upper molars:
| Size of molars mm | Molar number 6 | Molar number 7 | Molar number 8 |
| High crown of teeth | 7.5 | 7 | 6.5 |
| Near and far from the tooth crown | 10 | 9 | 8.5 |
| Outside inside the tooth crown | 11 | 11 | 10 |
| Total high |
18 |
17.5 | 19.5 |
| Age of growth | 6 | 12 | 18+ |
About the lower molars
The lower molars occupy the posterior portion of each side. Similar to the upper molars, their size will also gradually decrease. Below are some unique characteristics of mandibular molars:
- Mandibular molars usually have two roots, one mesial and one distal.
- Lower molars usually have 4 large cusps and a smaller 5th cusp.
- The tooth crown has a greater mesiodistal dimension than the buccal-lingual dimension.
- Lower molars are teeth with two large cusps on the inside of equal size.
- Their mesial and distal cusps are also similar in size.
- The upper and lower first molars are both permanent teeth that erupt at the age of 6. They are just distal to the second molar. They also mark the beginning of the mixed dentition milestone. That means with the simultaneous presence of both baby teeth and permanent teeth on the dental arch.
See more: TOP CERAMIC TEETH LINES THAT ARE POPULAR AT BEDENTAL? HOW ARE THE DIFFERENT SERIES OF PORCELAIN?
Below is a table of size and age of eruption of lower molars:
| Size of molars mm | Molar number 6 | Molar number 7 | Molar number 8 |
| High crown of teeth | 7.5 | 7 | 7 |
| Near and far from the tooth crown | 11 | 10 | 10 |
| Outside inside the tooth crown | 10.5 | 10.5 | 9.5 |
| Total high | 21.5 | 20 | 18 |
| Age of growth | 6 | 12 | 18+ |
Learn about premolars
In addition to asking “What are molars in Vietnam?”, people are also curious about premolars and their role in oral health. In English, premolars are called by another name Bicuspid – two-cushion teeth. However, not all premolars have two cusps, so this name is not widely used.
Time of eruption of premolars
Each of us will have a total of 8 premolars on the dental arch. Premolar teeth will grow to replace baby molars. They will grow between 9 and 11 years old, before the 2nd molars erupt.
The upper and lower first premolars erupt relatively evenly, usually by age 9. Next are the second premolars that erupt around age 11.
Quantity
In primitive humans there would be 4 premolars in each quadrant, or 16 per person. Over time, the central premolars were lost. Paleontologists call these intermediate premolars 3rd premolars and 4th premolars.
Shape and function
Premolars grow in the position between canines and molars on the dental arch. In terms of morphology, they are considered a transition between canines and molars. And as we know, canine teeth have a wedge-shaped cusp, responsible for the function of biting or tearing.
While molars have many cusps and a wide chewing surface. They will take on the function of chewing and grinding,
About the upper premolars
Outstanding features of the upper premolars are:
- The upper 1st and 2nd premolars are more similar to each other than the lower teeth.
- The upper premolars will have two large, raised cusps of equal size. This is completely different from the lower molars.
- If viewed from the chewing side, the premolars will have a buccolingual dimension larger than the mesiodistal dimension.
Below is a table of sizes and growth ages of the upper premolars:
| Size mm | Premolar 1 | Premolar 2 |
| High crown of teeth | 9.3 | 8.8 |
| Near and far from the tooth crown | 7.5 | 9.5 |
| Outside inside the tooth crown | 9.7 | 9.5 |
| Total high | 22.5 | 22.2 |
| Near and far from the Premolar | 5.3 | 5.3 |
| Outside inside the Premolar | 8.7 | 8.8 |
| Age of growth | 9 | 10 |
About the lower molars
Mandibular premolar number 1 is likened to a canine tooth. The second lower molar is like a miniature molar.
The characteristics of premolars are:
- The size of the outer zone is much larger than the inner zone.
- The tooth crown has a buccal and lingual dimension approximately equal to the mesio-distal dimension.
- Seen from the side, the outer contour is much more inclined than the inner.
- The maximum prominence is in the occlusal third.
- The middle groove often curves inwards.
Here is a table of the size and age of teeth eruption for the lower premolars:
| Size mm | Premolar 1 | Premolar 2 |
| High crown of teeth | 9.5 | 9.0 |
| Near and far from the tooth crown | 7.8 | 7.8 |
| Outside inside the tooth crown | 8.5 | 9.0 |
| Total high | 24 | 24 |
| Near and far from the Premolar | 5.0 | 5.2 |
| Outside inside the Premolar | 7.3 | 7.7 |
| Age of growth | 9 | 10 |
Are molars replaced?
In addition to asking “What are molars in Vietnam?”, people are also curious about the replacement of molars. There will be cases where children’s molars will be replaced and not replaced, specifically:
See more: How much does tooth scaling cost at BeDental? 4 benefits of scaling teeth
Molars do change
These are the molars in the milk teeth. When it comes to age, it will loosen and fall out, leaving space for permanent teeth to grow. Most of the time, molars number 1, 2 on the upper and lower jaw will be molars with replacement. Age range is 10 – 12 years old.

Molars do not change
The molar that is not replaced is usually molar number 3. This is a permanent tooth and does not go through the process of replacing baby teeth. Therefore, you need to help your baby take care of and preserve these teeth carefully.
Do molars grow back?
In addition to asking “What are molars in Vietnam?”, people are also curious that “Do molars grow back?”. When molars have grown into permanent teeth, you need to take care of them carefully because once lost, they will not grow back. However, you don’t need to worry too much because if you lose teeth due to any reason, you can still get dentures.
Currently, there are many aesthetic restoration techniques for missing molars, ensuring both chewing function and aesthetics.
The above article has helped you answer the question: “What are molars in Vietnam?”. Contact BeDental if you want advice on appropriate methods to have more precious information, we will provide free help 24/7.
See more: Cavities Between 2 Molars (Interdental Caries) and Effective Treatment Methods
BEDENTAL - TOP STANDARD DENTISTRY SYSTEM
In HANOI
Address 1: 7B Thi Sach St, Ngo Thi Nham, Hai Ba Trung Dist, Ha Noi. - 0934.61.9090
Address 2: No 129 Hoang Ngan, Yen Hoa, Cau Giay Dist, Ha Noi. - 0934.61.9090
In HO CHI MINH
Address 1: 53 -55 -57 Pho Duc Chinh St, Nguyen Thai Binh, Dist. 1, Ho Chi Minh. - 0766.00.8080
Working: 9am - 8pm everyday
Website: https://bedental.vn/en/