Some elderly people are under the impression that tooth loss is inevitable as we become older. Adult teeth do not fall out naturally, whereas baby teeth do. Seniors tooth loss is not inevitable. While ageing and time can lead to a decline in oral health, age is not a factor in tooth loss or other conditions. Find out how to maintain your teeth for life!
Major causes of seniors tooth loss
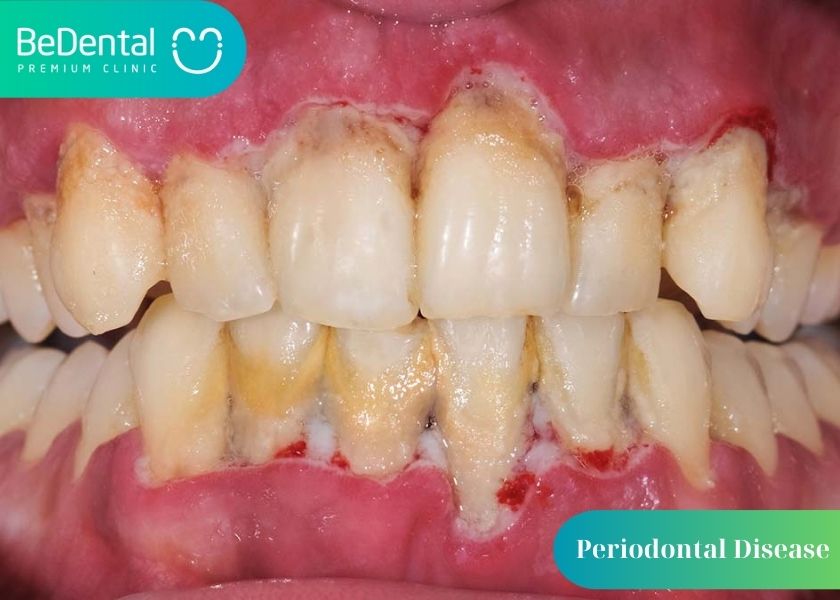
Major causes of seniors tooth loss: Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease, which sterilizes the mouth’s supporting tissues and frequently results in tooth loss, is the most common cause of seniors tooth loss. Because plaque and tartar build up over time and because maintaining good oral hygiene may get harder as you age, periodontal disease becomes more prevalent as you get older. If your periodontal disease isn’t severe, you might only require a few tips to make routine brushing more easy, such as using an electric toothbrush. It’s crucial to continue receiving treatment and care at the dentist office if you already have periodontal disease.

An inflammatory condition of the gum and bone supporting tissues (peridontal tissues) around the teeth is known as periodontal disease. Two of the most prevalent periodontal conditions are:
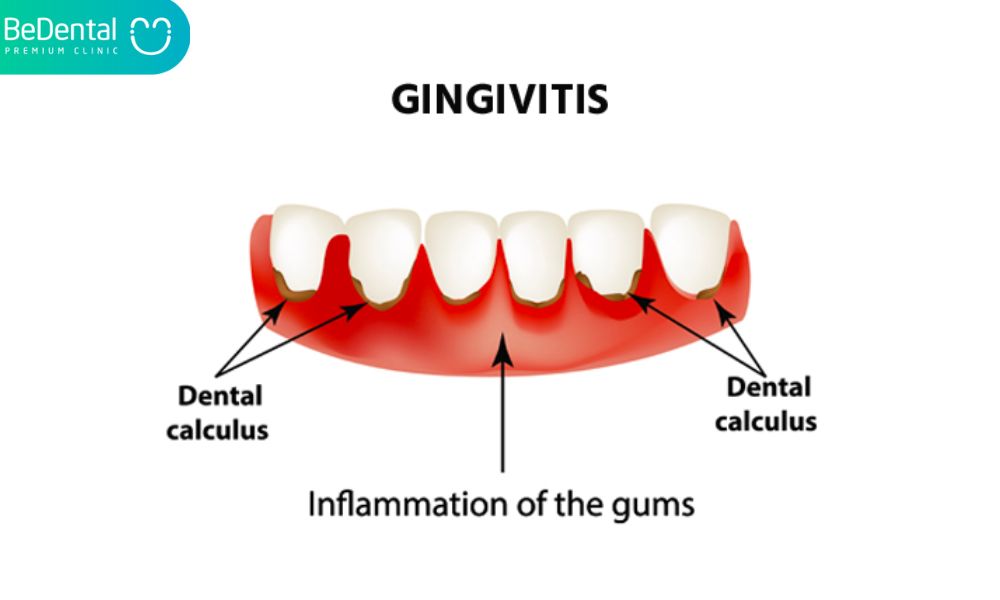
Major causes of seniors tooth loss: Gingivitis
Gum inflammation, swelling, and bleeding while brushing set off the early stages of gum disease. The most common causes of acute gingivitis are an infection, bacteria, or trauma. Chronic inflammation of the gum tissue around the teeth is linked to plaque that coats both the teeth and the gums. In the past, gingivitis was thought to represent the start of a long-term degenerative process that resulted in the loss of both gum and bone tissue surrounding the teeth. Gingivitis can now be reversed using practical oral hygiene methods.
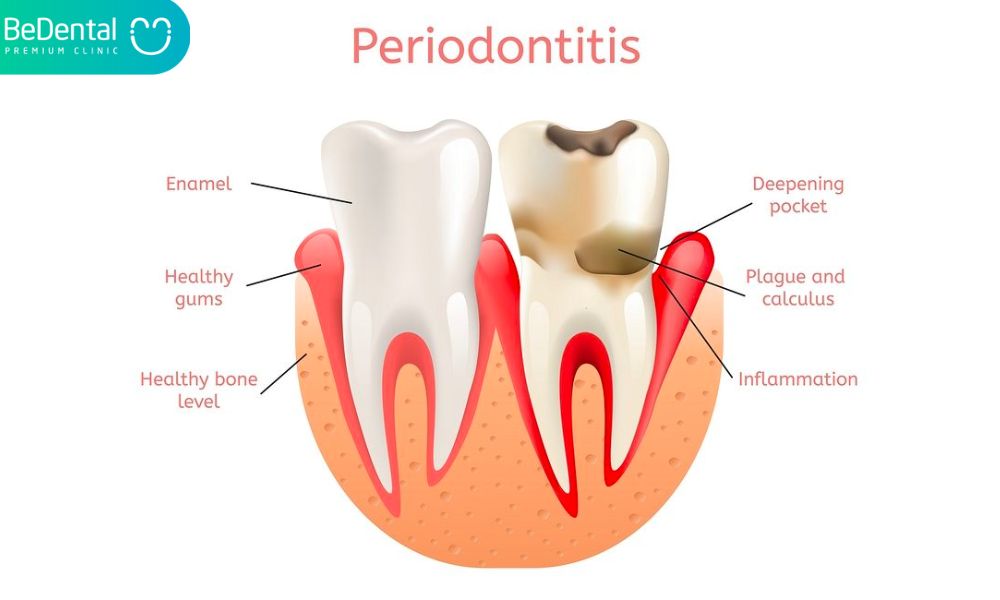
Major causes of seniors tooth loss: Periodontitis
The bone and tissues around the teeth are impacted by the inflammatory illness known as periodontitis.
Periodontitis, which is characterized by the development of pockets or gaps between the tooth and gums, happens when gum disease damages the bone and supporting tissue. Chronic periodontal damage from this might lead to tooth loss or loosening.
Due to its inability to cause pain, periodontal disease can be difficult to diagnose in its early stages. Early signs may just include bleeding gums while brushing teeth; when the condition worsens and the gums recede, the bleeding may stop, and there may be no other noticeable symptoms until the teeth start to feel loose. The majority of the time, periodontal disease responds to therapies, and while the degeneration is typically irreversible, dental care can halt its progression.
The rate of progression varies, and studies have connected it to other factors like leukemia, diabetes, HIV infection, poor immune systems, and Down syndrome.
Factors That Affect Periodontal Disease
Smoking and diabetes both worsen periodontal disease. Stress and food have also been connected to periodontal health. This may be due to the simple fact that stressed individuals are less likely to regularly practice decent oral hygiene. Most people may easily avoid gum disease by regularly brushing and flossing their teeth to remove plaque.
As if you needed another excuse to brush and floss often, periodontal disease has been linked to an increased vulnerability to systemic illnesses including cardiovascular disease, infective endocarditis (an infection in the heart valves or endocardium), bacterial pneumonia, and diabetes.
Nutritional Supplements
It’s common knowledge that eating well is important, but did you know that, in addition to all of the other health problems it may bring, a poor diet may also result in tooth loss? A diet low in calcium may increase the chance of tooth loss, and eating too many meals high in sugar, acid, or carbohydrates might unintentionally damage your teeth and gums. The mouth, teeth, and gums can suffer greatly from inadequate nutrition, which raises the risk of gum disease and other oral health issues.
Unhealthy Habits
Statistics show that tooth loss is twice as common among smokers than nonsmokers. Other harmful habits, such as drinking alcohol, using your teeth to open packages, or chewing hard sweets and ice, can weaken or fracture your teeth at any age, although the risks increase as you age.
How seniors can prevent tooth loss?
According to the NIDCR, over 27% of seniors over 65 had no teeth left. A study by CW Douglas found that 35.4 million Americans used dentures in 2000, and that number is predicted to increase to 37.9 million by 2020. According to the Silberg Center for Dental Science, tooth loss in seniors can have a detrimental effect on their quality of life on a variety of levels.
As a reason, it is recommended to use natural, non-invasive treatments to strengthen your teeth as you age. Elders should adhere to certain guidelines in order to preserve their dental health and, more importantly, prevent tooth loss, just as there are different ways to ensure that kids clean their teeth.
Keep an eye on what you eat
Too many sugary or starchy meals, according to the University of Rochester Medical Center, not only nourish you but also the bacteria in your teeth. For up to 20 minutes after eating, the acids produced when plaque and sugars in your mouth interact can erode your teeth. If this persists for a long time, the enamel protecting your teeth may degrade, which may result in tooth loss.
As a result, eating healthfully as you age is essential. These include foods like fiber-rich fruits and vegetables, green and black tea, sugar-free gum, and meals with fluoride. They all give your teeth essential nutrients and minerals that keep them strong.
Stop smoking
According to the NIDCR’s validated observatory studies, older adults who smoke are more likely to have fewer or no teeth left over over time. Smoking lowers immunity, which makes gum disease more challenging to recover from, according to the CDC. The bone and tissue that hold your teeth in place can be destroyed by periodontitis, a kind of gum disease, which can lead to tooth loss.
You need to stop smoking if you want to prevent your choppers from suffering from your addiction, especially if you assume that the longer you live, the more you smoke.

Replace missing teeth and go to the dental clinic more frequently
Many studies show that teeth gradually move out of position if there are gaps between them. These changes happen gradually, so you might not notice them, yet they weaken the gums and teeth. This suggests that if you’ve already lost one or more teeth, you should see a dentist regularly to prevent further loss. Additionally, dental visits are advised every six months by medical professionals, but you should go more regularly because older teeth are more fragile.
It takes work to age smoothly; it does not come easily. You should think about eating properly, avoiding gum disease, and giving up harmful habits like smoking while lowering tooth loss. The benefits of keeping healthy teeth include avoiding the high cost of replacement and continuing to be able to eat hard foods into old age.
Q&A
Is it normal for seniors tooth loss?
In the case of elders, tooth loss is a normal phenomenon that comes with growing older. Of course, seniors’ lifelong oral hygiene practices will play a significant part in preventing tooth loss, but there are other factors to consider as well.

What disease causes seniors tooth loss?
Periodontitis, it’s more severe form, can cause bone loss, gum tissue separation from the tooth, and eventual tooth loss. Most cases of periodontal disease occur in adulthood. The two main dangers to oral health are periodontal disease and tooth decay.
How can I strengthen my older teeth?
Follow 5 tips below daily to keep your teeth healthy:
- Avoid foods that harm your teeth.
- Eat more enamel-strengthening foods.
- Brush at least twice daily.
- Stop the grinding or clenching.
- Have regular dental checkups.
What vitamins are good for strong teeth?
Consume enough vitamin D and calcium to get your bones and teeth stronger, which helps limit the risk of dental diseases. Add eggs, seafood, and dairy products, which all contain vitamin D, to your diet.
The above article has helped you reveal everything about seniors tooth loss. Contact Bedental if you want advice on appropriate methods to have more precious information, we will provide free help 24/7.
More about seniors tooth loss
Dental Implant Care and 6 Common Concerns
The Purpose, Risks, and 4 Steps of Dental X-Rays that You Should Know
Porcelain Veneers and 3 factors influence the price of Porcelain Veneers
Tartar and 6 ways to prevent its return
Tư vấn chuyên môn bài viết:
BÁC SĨ DƯƠNG THỊ THÙY NGA

 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt 한국어
한국어 日本語
日本語 中文 (中国)
中文 (中国)



Pingback: Wisdom tooth removal: 4 things you must know – Be Dental
Pingback: SIGNS OF DENTAL INFECTION/BACTERIA AND 4 TREATMENT WAYS – Be Dental