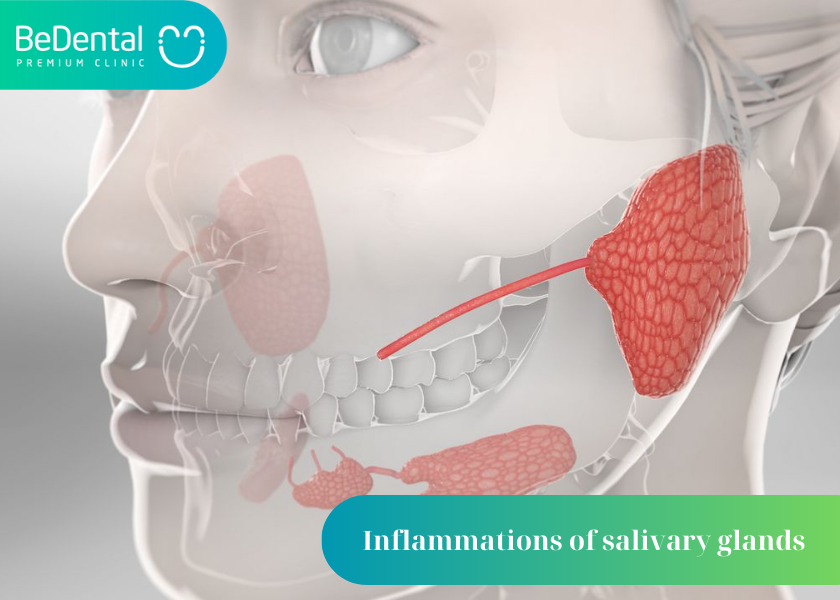
Salivary glands are a bacterial infection of the salivary glands, usually due to obstructed stones or decreased gland secretion. Symptoms are swelling, pain, redness and tenderness. Diagnosis is clinical, CT, ultrasound, and MRI can help determine the cause.
Tư vấn chuyên môn bài viết:
BÁC SĨ DƯƠNG THỊ THÙY NGA
What are salivary glands?
What are salivary glands? The salivary gland, also known as the salivary gland located in the mouth, is a system of small glands that produce and excrete saliva. Saliva is a liquid produced by the salivary glands and plays an important role in the respiratory process.
There are three main types of salivary glands in the mouth:
- Minor salivary glands: These are the largest glands and are usually located under the skin throughout the face and neck.
- Arcuated salivary glands: These are small glands located around the stromal tissues (nerves) that will provide saliva to help moisten and lubricate soft tissues during swallowing.
- Custom salivary glands: These are salivary glands located in the oral cavity, lips and nose. They also secrete saliva when we chew food or have the urge to chew.
Saliva contains starch and amylase enzymes to support food digestion, providing mineral salts and some antibacterial substances. Saliva helps clean the mouth and reduces food slippage and protects the gums and oral mucosa from bacteria.
Types of salivary gland inflammation
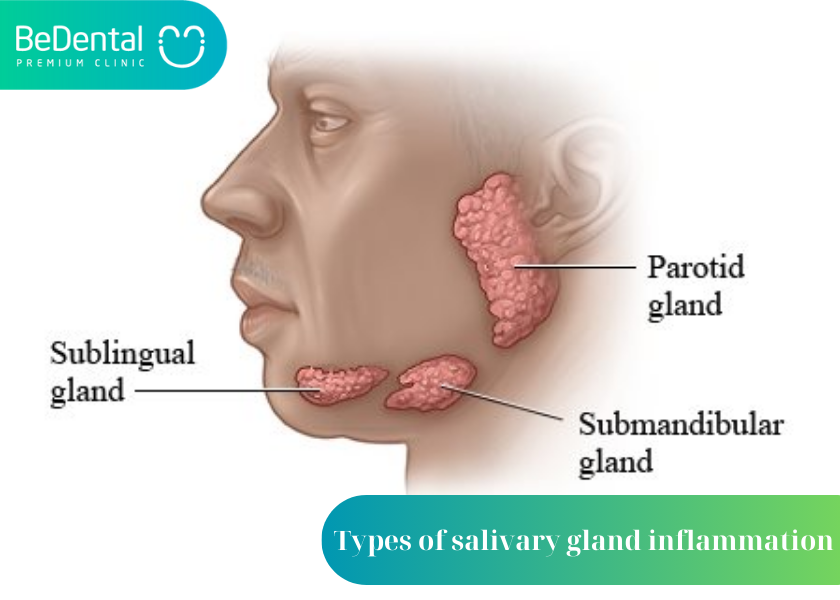
According to pathology, salivary gland infections often occur in 3 main salivary glands:
- Parotitis: An infection of the salivary glands located on the cheeks and in front of the ears. This is the body’s most important salivary gland.
- Submandibular salivary gland inflammation: Is an infection of the salivary glands located under the jaw. These are the second largest salivary glands.
- Submandibular salivary gland inflammation: Is an infection of the salivary glands located on both sides of the tongue and under the floor of the mouth. This is the smallest of the major salivary glands.
See more: What is tongue scraping? 10 things you need to know about tongue cleaning
Causes of salivary gland inflammation
What is the cause of salivary gland inflammation? Salivary gland inflammation is often caused by bacterial infection. Staphylococcus aureus is considered the most common cause of salivary gland inflammation and other bacteria such as: Streptococci, coliform and other anaerobic bacteria. In addition, it can also come from the following factors:
- Oral hygiene is not clean.
- Have ever had radiotherapy to the head and neck area.
- Have salivary gland stones.
- Salivary ducts are blocked by mucus.
- Malnutrition and dehydration are also some of the causes of salivary gland inflammation.
When suffering from inflammation of the salivary glands, patients rarely experience complications. However, if the inflammation of the salivary glands is not treated, pus can accumulate and form an abscess in the salivary gland. Salivary gland inflammation caused by a benign tumor can cause the glands to enlarge. Melanoma can grow quickly and cause difficulty with facial movements.
Harmful effects of salivary gland inflammation
Salivary gland inflammation, commonly known as sialadenitis, is an inflammation of the salivary glands in the mouth. Salivary gland inflammation can cause the following symptoms:
- Pain and swelling: Salivary gland inflammation is often accompanied by pain and swelling in the inflamed glands. Pain can make eating and talking difficult.
- Salivary dysfunction: Inflammation of the salivary glands will reduce the secretion of saliva. This can cause difficulty with salivation and dry mouth. Saliva provides lubrication and protects the oral mucosa and teeth from infection, so salivary dysfunction can increase the risk of dental and oral mucosal diseases.
- Infection: If salivary gland inflammation is not treated promptly, it will cause infection. The infection will spread and cause severe inflammation, pain and swelling at times. If not treated early, the infection will spread to surrounding areas and cause even more serious consequences.
- Sialolithiasis: This is a condition in which stones form in the salivary glands. Stones can block salivary drainage and cause inflammation of the salivary glands. If the stone is left untreated, it will cause pain and increase the risk of infection.
To diagnose and treat sialadenitis, it is important to seek examination and treatment by a doctor or oral and dental health professional to prevent potential harm and relieve pain.
Symptoms of salivary gland inflammation
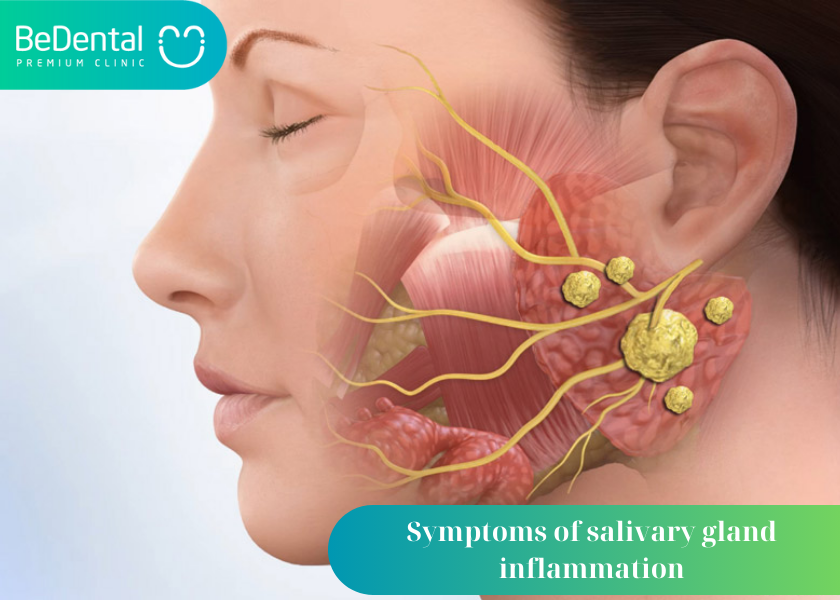
Signs and symptoms of salivary gland inflammation, patients may have the following signs and symptoms:
- Patients experience sudden swelling of the parotid gland while swallowing. Initially, the symptoms were similar to mumps, so many people were confused.
- There is a bad smell and an unusual feeling in the mouth.
- After parotid gland swelling, there will be whole body signs such as fever and fatigue.
- Feeling pain or discomfort when opening your mouth.
- Can’t open my mouth wider.
- Your mouth feels dry
- Pus appears in the mouth
- Feeling pain in the mouth
- Facial pain
- The jaw in front of the ear, under the jaw or at the top of the mouth shows signs of swelling and redness.
- Swollen neck or face
These common signs and symptoms may occur with sialadenitis. However, the symptoms of salivary gland inflammation are often confused with symptoms of other diseases.
Therefore, patients need to see a doctor to get an accurate diagnosis. In addition, people with salivary gland inflammation who have signs of difficulty breathing, high fever, difficulty swallowing or other increasingly serious symptoms should immediately go to the hospital for examination and treatment.
See more: 4 STANDARDS FOR EVALUATING BEAUTIFUL MEN’S TEETH THAT YOU NEED TO KNOW
Complications of salivary gland inflammation
If salivary gland inflammation is not treated promptly, it can cause dangerous complications such as:
- Salivary gland abscess: An infection that is not controlled or treated promptly for a long time can cause pus accumulation and complications into an abscess.
- Salivary gland hypertrophy: Chronic salivary gland infection can lead to salivary gland hypertrophy. Besides, salivary gland enlargement can be due to autoimmune or neoplastic causes
- Airway obstruction: Uncontrolled infection can lead to throat swelling and airway obstruction. Saliva infections that spread to the facial bones can be difficult to control.
Methods of diagnosing salivary gland inflammation
The most common methods of diagnosing salivary gland inflammation today include: ultrasound, CT-scan, MRI, biopsy; endoscopy, and remove pus from the salivary gland duct in cases of suspected salivary gland infection.
Swelling due to blockage of salivary ducts causes pain related to eating or drinking foods that increase salivation. To differentiate between some possible causes of enlarged salivary glands, your doctor may use other tests including:
- Biopsy: Performed by taking a sample of salivary gland tissue and examining it under a microscope.
- Endoscopy: Performed by inserting an endoscope equipped with a tiny camera into the salivary gland ducts for observation.
- X-ray: Indicated in cases where the doctor cannot make a diagnosis during a physical examination. X-rays may be performed after using contrast that can be seen on the X-rays that have been injected into the salivary glands and ducts.
- Computed tomography (CT) and ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): indicated in cases of suspected infection to identify inflammation.
- Culturing pus from the salivary duct: If the doctor is able to squeeze pus from the inflamed salivary duct, the bacteria will be cultured in the laboratory.
- Blood test: To detect increased amylase in blood and urine, decreased white blood cells, decreased neutrophils if inflammation is caused by a virus, or increased neutrophils for bacterial causes.
Is salivary gland inflammation contagious?
Is salivary gland inflammation contagious? According to experts, sialadenitis is not contagious and in fact it has been proven that there is no second case of infection even if the person with sialadenitis is a family member. The reason this can be confirmed is:
The salivary glands consist of two main parts: small salivary glands and large salivary glands. Salivary gland tumors are mostly benign and do not spread to other parts of the body. Malignant cells will transform into cancer to spread in the patient’s body, but these malignant cells are never present in the patient’s salivary glands, so you can completely rest assured.
So with the question: Is salivary gland inflammation contagious? then the answer is Salivary gland inflammation is not contagious from person to person.
But don’t think that salivary gland cancer is not contagious because you subjectively do not learn about the common causes of the disease. According to research, the groups of people most at risk of getting sick are those who have undergone radiation therapy to the head and neck area, workers or those exposed to a lot of radiation from manufacturing plants. , people who use a lot of phones are also at risk of parotid salivary gland cancer, so you need to pay close attention.
Although sialadenitis is not spread through daily contact, not even through kissing or oral sex, sialadenitis can originate from other agents, so when infected, the patient’s health will be seriously affected, and can even cause death if not detected early and treated promptly.
Herbs to treat inflammation of the salivary glands
Salivary gland inflammation is a common disease in patients suffering from respiratory diseases or diseases related to the mouth and throat. In addition to treatment with antibiotics and other anti-inflammatory drugs, some herbal medicines can help treat inflammation of the salivary glands. However, before using any herbal medicines, you should seek advice from your doctor or practitioner to ensure that they are suitable for your situation and do not cause side effects.
Below are some herbal medicines that can be used to help treat sialadenitis:
- Ginseng Root: Ginseng root has anti-inflammatory properties and can help reduce inflammation of the salivary glands. People often use ginseng as a drink or medicine.
- Honey Root: Honey Root has anti-inflammatory properties and helps strengthen the body’s immune system. People often use honey as a drink or as medicine.
- Witch hazel: Witch hazel has anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. People often use witch hazel as an essential oil or medicine.
- Fenugreek Root: Fenugreek root has anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. People often use clover as a drink or as medicine.
- Aloe vera root: Aloe vera root has anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. People often use roses in the form of drinking water or medicine.
Prevention of salivary gland inflammation
- Maintain good oral hygiene, brush your teeth regularly and properly, and clean between your teeth with dental floss…
- Use mouthwash after every meal to clean the tongue and oral cavity, eliminating disease-causing microorganisms.
- Avoid exposure to radiation sources from factories and plants.
- Don’t smoke and drink too much alcohol.
- Supplement necessary nutrients, eat enough nutrients and have a reasonable diet to strengthen the body’s resistance.
- Hands must be washed before eating and after going to the toilet.
- Drink a lot of water.
Things to note when suffering from inflammation of the salivary glands
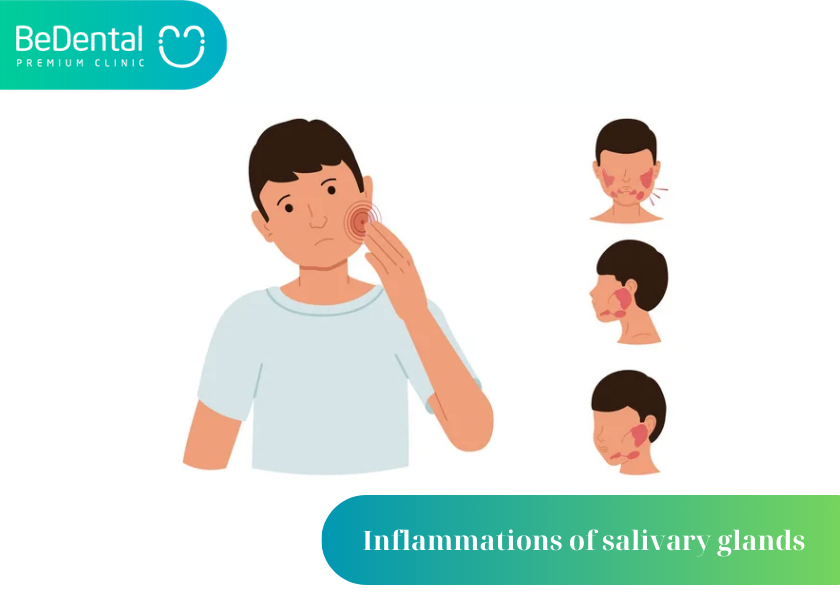
When you have salivary gland inflammation, please refer to the following measures to control the condition:
- Seek examination and advice from a doctor: First, consult a doctor or medical professional specializing in mouth and teeth to get a correct diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
- Drink plenty of water: Always add enough water to your body. Drinking enough water will help keep your mouth moist and enhance saliva function.
- Brush your teeth and use mouthwash: Washing your mouth every day is extremely necessary. Brushing your teeth at least twice a day and using an alcohol-free mouthwash can keep your mouth clean and reduce your risk of tooth decay.
- Eat a reasonable diet: Eat a diet high in fiber and avoid foods high in sugar and starch. Avoid chewing foods that are too cold and too hot or too cold to reduce the impact on the salivary glands.
- Rest and reduce stress: Helps the body have the necessary relaxation time and reduce mental stress. Stress can affect the salivary glands and increase the risk of sialadenitis.
- Examination and cleaning of stones: If inflammation of the salivary glands leads to stones in the salivary glands, the doctor should examine and clean the stones. This helps improve saliva flow and reduces the risk of inflammation.
- Follow your treatment: If your doctor prescribes medication or other treatments, follow your doctor’s instructions. Drink adequate amounts of water and use other oral hygiene products as directed by your doctor
The salivary glands, also known as the salivary gland located in the mouth, is a system of small glands that produce and excrete saliva. Saliva is a liquid produced by the salivary glands and plays an important role in the respiratory process.
See more: ROOT CANAL TREATMENT AND 2 THINGS TO DO AFTER ROOT CANAL TREATMENT
BEDENTAL - TOP STANDARD DENTISTRY SYSTEM
In HANOI
Address 1: 7B Thi Sach St, Ngo Thi Nham, Hai Ba Trung Dist, Ha Noi. - 0934.61.9090
Address 2: No 129 Hoang Ngan, Yen Hoa, Cau Giay Dist, Ha Noi. - 0934.61.9090
In HO CHI MINH
Address 1: 53 -55 -57 Pho Duc Chinh St, Nguyen Thai Binh, Dist. 1, Ho Chi Minh. - 0766.00.8080
Working: 9am - 8pm everyday
Website: https://bedental.vn/en/