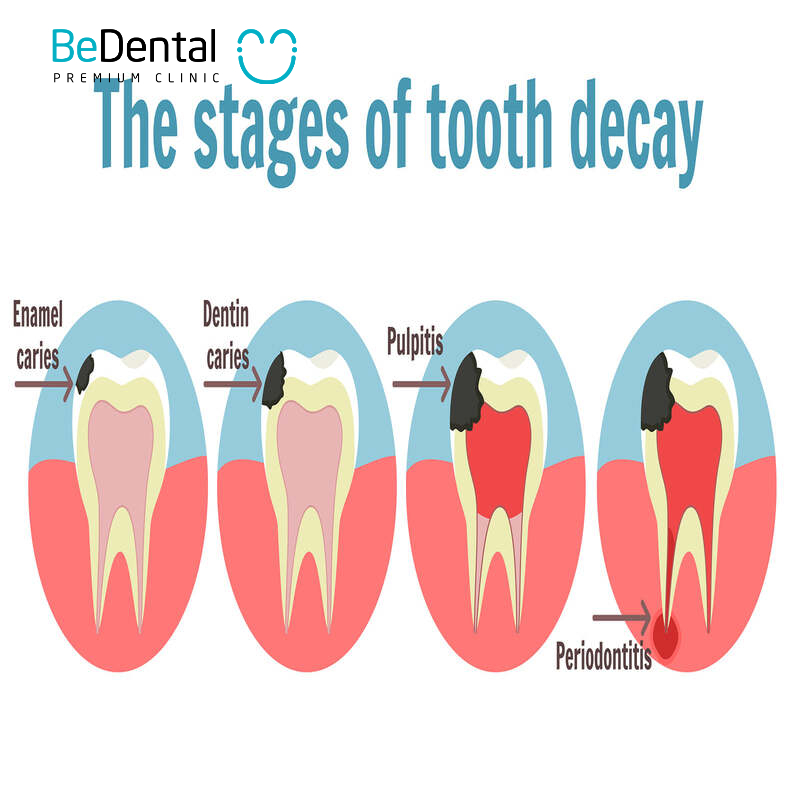
Tooth decay is one of the most common oral health problems worldwide, affecting approximately 60-90% of children and nearly 100% of adults in many countries. The stages of tooth decay progresses through four main stages: plaque formation, enamel decay, dentin decay, and pulp decay. Each stage has distinct characteristics and symptoms, requiring appropriate treatment measures to prevent more severe conditions.
Current State of Cavities by Age Group
Tooth decay is a prevalent oral health issue across all age groups in Vietnam. For children aged 6 to 12 years, about 70% have at least one decayed tooth, primarily due to high sugar consumption and inadequate oral hygiene awareness. Among adolescents (ages 13-19), this rate drops to nearly 60%, but remains concerning due to poor eating habits and a lack of brushing.
For adults (ages 20-40), around 40% have at least one decayed tooth, often linked to stress and an unhealthy diet. Meanwhile, the rate of cavities among the elderly (over 60 years old) is approximately 25-30%, primarily due to reduced saliva production and changes in diet and overall health.
Rate of Cavities in Children (Aged 6-12)
The prevalence of cavities in children aged 6 to 12 is a serious oral health issue in Vietnam. Statistics show that about 70% of children in this age group have at least one decayed tooth. The main cause is unhealthy eating habits, including excessive consumption of sugary foods and soft drinks. Furthermore, children’s oral hygiene awareness (Oral health tips for children) is limited, leading to improper brushing and infrequent flossing. This not only affects their oral health but can also cause pain, difficulty eating, and hinder their development.
Rate of Cavities in Adolescents (Aged 13-19)
Among adolescents, the cavity rate tends to decrease to nearly 60%. However, this situation remains alarming, as many teens continue to maintain poor eating habits and neglect dental hygiene. Sugary foods, carbonated drinks, and snacks are frequently consumed, while oral hygiene practices have not improved. Factors such as academic and social pressures lead many young people to overlook oral care routines, resulting in cavities and related issues. Without timely care, cavities can lead to more severe complications in the future.
Rate of Cavities in Adults (Aged 20-40)
In the adult age group (20-40 years), about 40% have at least one decayed tooth. The main causes stem from busy lifestyles and unhealthy diets. Many individuals frequently consume processed foods high in sugar and fat, contributing to plaque buildup and cavities. Additionally, stress and work pressures impact oral hygiene habits. Skipping regular dental check-ups and neglecting proper dental care can lead to more serious issues like gum disease and tooth loss.

Rate of Cavities in the Elderly (Over 60)
For the elderly, the cavity rate ranges from about 25-30%. The primary reason for this is reduced saliva production, which makes the mouth drier and increases the risk of cavities. Furthermore, changes in diet and overall health can also impact oral condition. Many older adults may struggle with eating and maintaining oral hygiene due to other health issues, such as diabetes or cardiovascular diseases. This makes oral care more essential than ever to maintain their health and quality of life.
Stages of Tooth Decay
It forms and progresses through four stages of tooth decay: from plaque formation to enamel decay, dentin decay, and pulp decay.
Stage 1: Plaque Formation- Stages of tooth decay
- Characteristics: The first stage in the development of cavities is the formation of plaque on the tooth surface. Plaque is a thin, sticky film made up of bacteria, dead cells, and food particles. If not regularly removed, plaque can harden into tartar, facilitating the growth of harmful bacteria.
- Causes: The primary cause of plaque formation is bacteria in the mouth and the consumption of sugary foods, which lead to fermentation and acid production. Unhealthy eating habits, such as consuming excessive sweets and sugary drinks, further increase the risk of plaque formation.
Stage 2: Enamel Decay
- Characteristics: In this stage, the tooth enamel begins to deteriorate, resulting in small holes appearing on the enamel surface. Enamel is the outer protective layer of the tooth, and when damaged, the tooth becomes weaker and more susceptible to harm.
- Symptoms: Patients may experience mild pain and sensitivity to temperature, especially when consuming hot or cold foods. These sensations are warning signs that the enamel has been compromised and requires timely care.
Stage 3: Dentin Decay
- Characteristics: In this stage, the cavity enlarges and begins to affect the dentin, the softer tissue beneath the enamel. Dentin (wikipedia) is more vulnerable than enamel, and its destruction can lead to pain and discomfort.
- Symptoms: Patients may experience severe pain and discomfort while eating, particularly when consuming hot, cold, or sweet foods. This discomfort can worsen if not treated promptly, leading to chronic pain and negatively impacting quality of life.
Stage 4: Pulp Decay
- Characteristics: This is the most severe stage when the cavity extends into the dental pulp, which contains nerves and blood vessels. When the pulp becomes infected, not only does the tooth hurt, but there’s also a risk of the infection spreading to other areas of the mouth and body.
- Symptoms: Patients will feel persistent, frequent pain, and there may be swelling in the gums. This condition causes discomfort and affects the patient’s ability to eat and communicate.
Causes of tooth decay in each stage
Here are the main causes of tooth decay categorized by age groups:
Causes of tooth decay in Children (Ages 0-12)
Children are particularly vulnerable to tooth decay due to their developing teeth and dietary habits. Sugary foods and beverages, combined with inconsistent brushing, create an environment conducive to cavities. Establishing good oral hygiene practices early on, such as regular brushing with fluoride toothpaste and limiting sugary snacks, is essential. Parents play a crucial role in guiding their children’s dental care, ensuring they visit the dentist for regular check-ups and cleanings to monitor dental health and prevent decay.
Causes of tooth decay in Teenagers (Ages 13-19)
Teenagers face unique challenges regarding oral health, often influenced by peer pressure and busy lifestyles. The consumption of sugary snacks and soft drinks, alongside the neglect of proper dental hygiene, increases their risk of cavities. Additionally, orthodontic treatments like braces can make it more difficult to maintain good oral hygiene. Encouraging teenagers to adopt healthier eating habits and prioritize their dental care is vital for preventing tooth decay during these formative years.
Causes of tooth decay in Adults (Ages 20-64)
In adulthood, the pressures of work and family can lead to neglect of dental health. Busy schedules may result in missed dental appointments and inconsistent oral hygiene routines. Adults are also more likely to experience dietary changes, such as increased snacking on unhealthy foods, which can lead to cavities. Moreover, certain health conditions and lifestyle factors, like smoking, can further exacerbate dental issues. Maintaining regular dental visits and practicing effective oral hygiene are critical for adults to preserve their dental health.
Causes of tooth decay in Seniors (Ages 65 and Older)
Seniors face distinct challenges concerning oral health, often stemming from age-related changes and health conditions. The natural wear of tooth enamel makes teeth more susceptible to decay, while medications that cause dry mouth can decrease saliva production, a vital factor in cavity prevention. Physical limitations may hinder seniors’ ability to maintain effective oral hygiene, increasing their risk of dental problems. Encouraging regular dental check-ups and adopting strategies to improve oral hygiene can significantly enhance the dental health of seniors.
The symptoms of tooth decay among different age groups
The symptoms of tooth decay can vary significantly among different age groups. In children (ages 0-12), common signs include pain, especially when consuming hot or cold foods and beverages. They may also shy away from sweets and exhibit noticeable color changes in their teeth, such as brown or black spots. For teenagers (ages 13-19), sensitivity to sweet or acidic foods is typical. Bad breath may develop due to bacterial buildup, along with visible spots or holes on the teeth, indicating the presence of cavities.
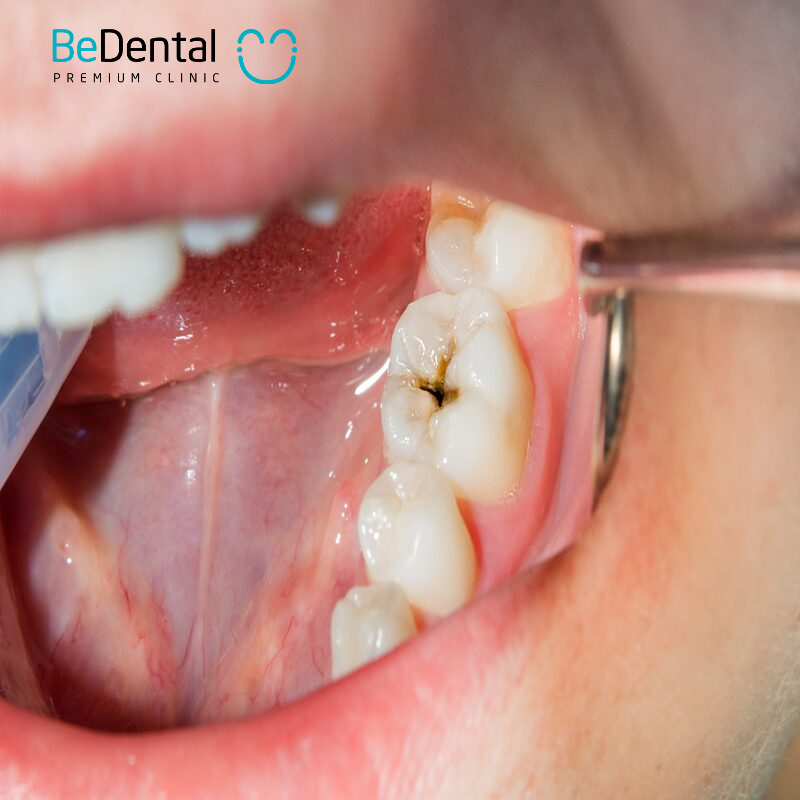
Adults (ages 20-64) often experience toothaches when eating, along with swollen and red gums; in severe cases, they may face tooth loss. Finally, in the elderly (ages 65 and older), persistent pain and sensitivity to food remain prevalent, coupled with declining gum health and weakened teeth that are more susceptible to decay and breakage. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for timely intervention to prevent more serious dental issues.
Effective Treatment Measures
Preventing cavities is crucial not only for protecting oral health but also for improving quality of life. A proper care regimen combined with good hygiene habits will minimize the risk of cavities and other oral health issues.
Practice Proper Oral Hygiene
- Brushing Guidelines: It is essential to brush at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste. Proper brushing helps remove plaque and bacteria, preventing cavity formation.
- Flossing: Daily flossing is important to clean between teeth where toothbrushes cannot reach. This helps prevent the buildup of plaque and food particles.
Maintain a Balanced Diet
- Food Choices: Consume nutrient-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, and dairy products, while limiting sugary foods and carbonated drinks. These foods can lead to plaque formation and cavities.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking water is crucial for rinsing the mouth and maintaining moisture, preventing dry mouth.
Dental Care
- Regular Check-ups: Visit a dentist for oral health check-ups at least twice a year. Professionals can help detect early signs of cavities and provide thorough dental cleanings.
- Use Support Products: Products containing fluoride and antibacterial mouth rinses can help strengthen enamel and prevent bacterial growth.
Home Treatment
- Use Cleaning Products: Products like interdental brushes, water flossers, or cleaning gels can improve oral hygiene and remove plaque from hard-to-reach areas.
- Home Remedies: Some home remedies, such as rinsing with saltwater or lemon juice, can help support treatment and enhance oral health.
From the initial plaque formation to pulp decay, each stage presents different risks and symptoms that directly impact health and quality of life. By implementing effective preventive measures and seeking timely treatment, we can protect our oral health and minimize the negative consequences of cavities. Focusing on oral hygiene, a balanced diet, and regular dental check-ups will help maintain a healthy, confident smile.
BeDental is a reputable dental clinic in Vietnam
BeDental is a reputable dental clinic in Vietnam that offers comprehensive examination and treatment for cavities for patients of all ages. The clinic’s commitment to providing high-quality dental care is evident through its team of experienced professionals, advanced technology, and patient-centered approach.
For those seeking further consultation regarding dental examination services, please visit BeDental’s locations in Hanoi or Ho Chi Minh City. You can also reach us at our hotline: (+84) 934.61.9090 / (+84) 899.555.636 or through our Facebook page, BeDental, for prompt and accurate assistance.

 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt 한국어
한국어 日本語
日本語 中文 (中国)
中文 (中国)