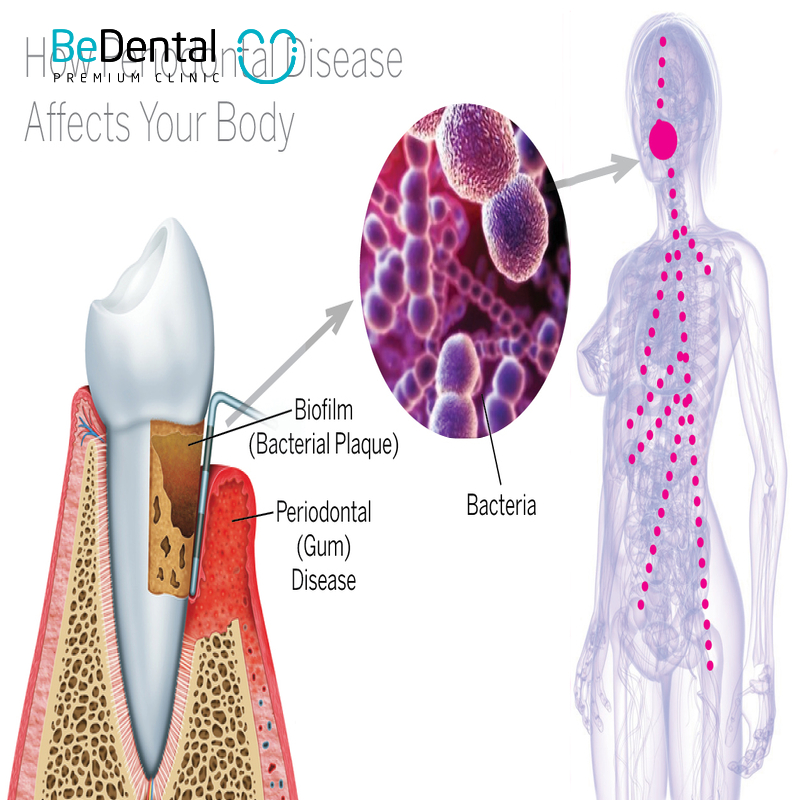
The link between periodontal disease and systemic conditions is garnering increasing attention from the medical research community. Numerous studies have shown that periodontal disease not only impacts oral health but may also elevate the risk of developing other serious conditions. A study published in the American Heart Association journal revealed that individuals with periodontal disease have a 19% higher risk of cardiovascular disease compared to those without the condition.
Furthermore, research from the Journal of Diabetes Research found that periodontal disease can impair blood sugar control in diabetic patients, leading to a higher risk of complications. These findings emphasize that oral care is not just about maintaining healthy teeth but is closely linked to overall health.
Definition of periodontal disease and the link between periodontal disease and systemic conditions
Periodontal disease is a chronic inflammatory condition affecting the supporting tissues of the teeth, including the gums, bone, and periodontal ligaments. The primary cause is the buildup of bacterial plaque on the teeth and beneath the gum line. If left untreated, periodontal disease can lead to gingivitis, destruction of surrounding tissues, and ultimately tooth loss.
Scientific evidence increasingly supports the link between periodontal disease and various systemic conditions (from National Library of Medicine)
- Cardiovascular Disease: Studies indicate that chronic inflammation caused by periodontal disease can contribute to the formation and progression of atherosclerotic plaques, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Bacteria from inflamed gums can enter the bloodstream, causing inflammation in the arteries.
- Diabetes: Research highlights a two-way relationship between diabetes and periodontal disease. Diabetes impairs the body’s ability to fight infections, raising the risk of periodontal disease, while periodontal inflammation can elevate blood sugar levels, making diabetes management more difficult.
- Respiratory Disease: Bacteria from the mouth can be inhaled into the lungs, leading to respiratory infections like pneumonia or exacerbating conditions such as COPD. Periodontal disease increases the risk of lower respiratory tract infections.
- Pregnancy Complications: Studies have shown that pregnant women with periodontal disease are at higher risk for preterm birth, low birth weight, and other pregnancy complications due to systemic inflammation.
This evidence underscores that periodontal disease extends beyond the mouth and can have serious implications for overall health, making prevention and treatment crucial.
Systemic health conditions linked to periodontal disease
Here is a detailed analysis of how periodontal disease relates to key systemic health issues, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, respiratory conditions, and pregnancy complications.
The link between periodontal disease and cardiovascular health
Periodontal disease is not only an oral issue but is closely associated with systemic conditions, particularly cardiovascular disease. Periodontal infections can cause widespread inflammation, increasing the risk of severe conditions such as endocarditis and atherosclerosis. The presence of oral bacteria in the bloodstream can lead to inflammation and damage to blood vessels.
- Connection: Periodontal infections trigger systemic inflammation, heightening the risk of heart disease.
- Mechanism: Bacteria from inflamed gums can enter the bloodstream, leading to conditions like endocarditis and atherosclerosis.
The link between periodontal disease and diabetes
In diabetes, there is a clear two-way relationship. Diabetic individuals are more susceptible to periodontal disease due to a weakened immune response, while inflammation from periodontal disease worsens blood sugar control, leading to higher systemic inflammation.
- Two-way interaction: Diabetes increases the risk of periodontal disease, and periodontal disease worsens blood sugar control.
- Mechanism: Bacteria from periodontal disease raise systemic inflammation, complicating blood sugar management.
The link between periodontal disease and respiratory health
Periodontal disease is also linked to respiratory diseases, as bacteria from the mouth can be inhaled into the lungs, leading to respiratory infections like pneumonia or exacerbating chronic conditions like COPD.
- Connection: Oral bacteria can be inhaled, causing respiratory infections such as pneumonia.
- Mechanism: Periodontal disease can worsen conditions like COPD by increasing infection risks.
The link between periodontal disease and pregnancy complications
In terms of pregnancy, periodontal disease has been recognized as a contributing factor to adverse outcomes, including preterm birth and low birth weight. The inflammatory response from periodontal disease can affect both maternal and fetal health, increasing the likelihood of complications.
- Connection: Periodontal disease is associated with preterm birth, low birth weight, and other pregnancy complications.
- Mechanism: Oral inflammation can lead to systemic inflammatory responses, impacting both the mother and the fetus.
Mechanisms linking periodontal disease to systemic health conditions
Bacteria from the mouth, particularly those that cause periodontal disease such as Porphyromonas gingivalis and Tannerella forsythia, can enter the bloodstream through inflamed gum tissues. Once these bacteria breach the body’s natural defenses, they can spread to other organs. The inflammatory response triggered by periodontal disease extends beyond the mouth, contributing to chronic inflammation that increases the risk of various systemic diseases like cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and respiratory disorders.

- Pathway: Oral bacteria enter the bloodstream through inflamed gum tissues.
- Impact: Inflammation from periodontal disease spreads to other parts of the body, raising the risk of systemic conditions.
This chronic inflammation fosters a cycle of damage, leading to the development of conditions like atherosclerosis, impaired blood sugar control, and heightened respiratory infections. The presence of oral bacteria in the bloodstream can also lead to conditions such as endocarditis or exacerbate existing diseases. Therefore, maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial not only for oral health but also for preventing broader health issues.
Key periodontal pathogens linked to systemic health conditions
Specific bacteria involved in periodontal disease play a critical role in increasing the risk of systemic health issues. Below are some of the main periodontal pathogens and their effects on overall health:
Porphyromonas gingivalis- The link between periodontal disease and systemic conditions
- Porphyromonas gingivalis (wikipedia): This key pathogen in periodontal disease can infiltrate deep gum tissues and produce enzymes that destroy surrounding tissues and bone.
- Systemic effect: P. gingivalis can enter the bloodstream, leading to vascular inflammation and promoting the development of atherosclerosis, which raises the risk of heart disease.
Tannerella forsythia-The link between periodontal disease and systemic conditions
Tannerella forsythia: Typically present in advanced stages of periodontal disease, this bacterium is involved in chronic inflammation.
Systemic effect: T. forsythia can cause widespread inflammation after entering the bloodstream, contributing to conditions such as diabetes and respiratory diseases.
Treponema denticola-The link between periodontal disease and systemic conditions
Treponema denticola: A member of the “red complex” of bacteria, known for tissue destruction in periodontal disease.
Systemic effect: T. denticola increases systemic inflammation, affecting cardiovascular and respiratory health.
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans-The link between periodontal disease and systemic conditions
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans: Often associated with rapidly progressing periodontal disease, this bacterium can destroy the supporting tissues around the teeth.
Systemic effect: A. actinomycetemcomitans is linked to infective endocarditis when it enters the bloodstream, raising the risk of cardiovascular issues.
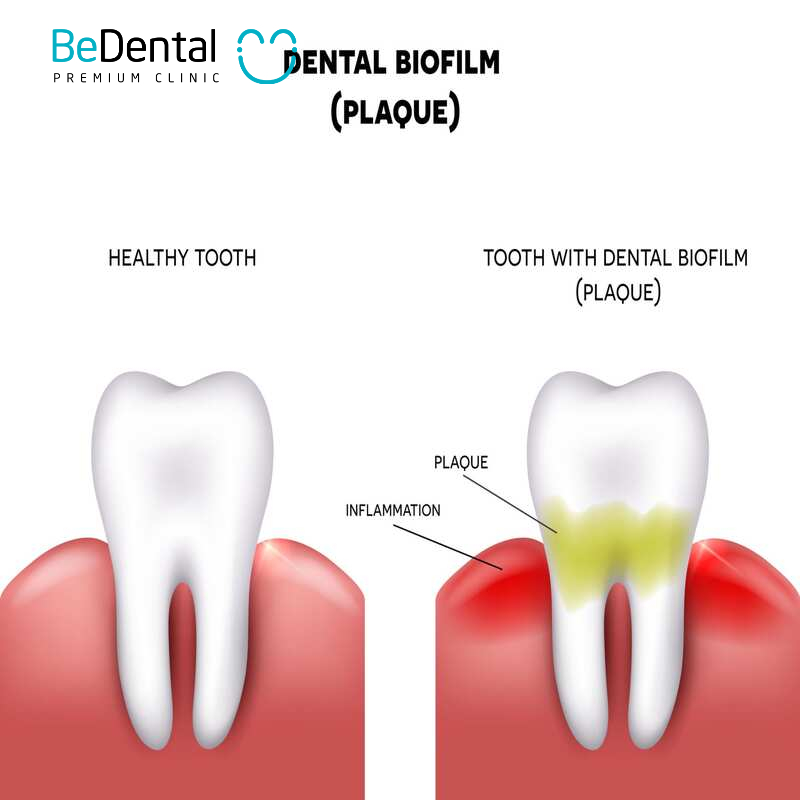
Fusobacterium nucleatum-The link between periodontal disease and systemic conditions
Fusobacterium nucleatum: Found in periodontal disease and other oral infections.
Systemic effect: F. nucleatum has been linked to preterm birth and other pregnancy complications, as it can spread beyond the oral cavity.
These pathogens not only cause localized oral inflammation but also have the potential to travel through the bloodstream, affecting various organs and contributing to the development of systemic diseases. Controlling these bacteria is essential in reducing the risk of systemic health conditions.
Preventing and managing periodontal disease to protect overall health in Vietnam
To maintain both oral and systemic health, proper oral hygiene is essential in preventing and managing periodontal disease to protect overhealth in Vietnam. This includes brushing at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing to remove plaque and food particles between teeth, and using mouthwash to reduce bacterial buildup.
- Practice proper oral hygiene: brush your teeth, floss, and use mouthwash
- Schedule regular dental check-ups to catch and treat gum disease early.
- If you have diabetes or heart disease, pay extra attention to your oral health.
- Ensure coordinated care between your dentist and specialist.
Regular dental visits are key for detecting and addressing issues like gum disease early on. For individuals with diabetes or heart conditions, maintaining good oral health is especially important, as oral infections can worsen other health issues. Finally, collaboration between your dentist and specialist will ensure your oral care is well-managed, supporting your overall health.
Bedental is a leaving dental clinic in Vietnam
Bedental specializes in tartar removal, including scaling and polishing procedures that ensure thorough cleaning of the teeth and gums. Regular dental check-ups and cleanings at Bedental are essential to prevent tartar buildup and promote long-term oral hygiene.
For those seeking further consultation regarding dental examination services, please visit BeDental’s locations in Hanoi or Ho Chi Minh City. You can also reach us at our hotline: (+84) 934.61.9090 / (+84) 899.555.636 or through our Facebook page, BeDental, for prompt and accurate assistance.