Periodontitis, also known as periodontal disease, is a common oral health condition that affects both adults and children. The disease can be detected early if you notice some abnormal signs such as bleeding gums, swollen gums, etc. So what is Periodontitis? What are the causes of Periodontitis? How is Periodontitis treated? Let’s find out in the article below!
What is Periodontitis? Early Detection of Periodontitis Through These Signs
What is Periodontitis? Periodontitis is a condition where the areas around the teeth become inflamed. Periodontitis is usually divided into 2 types: Periodontitis and gingivitis.
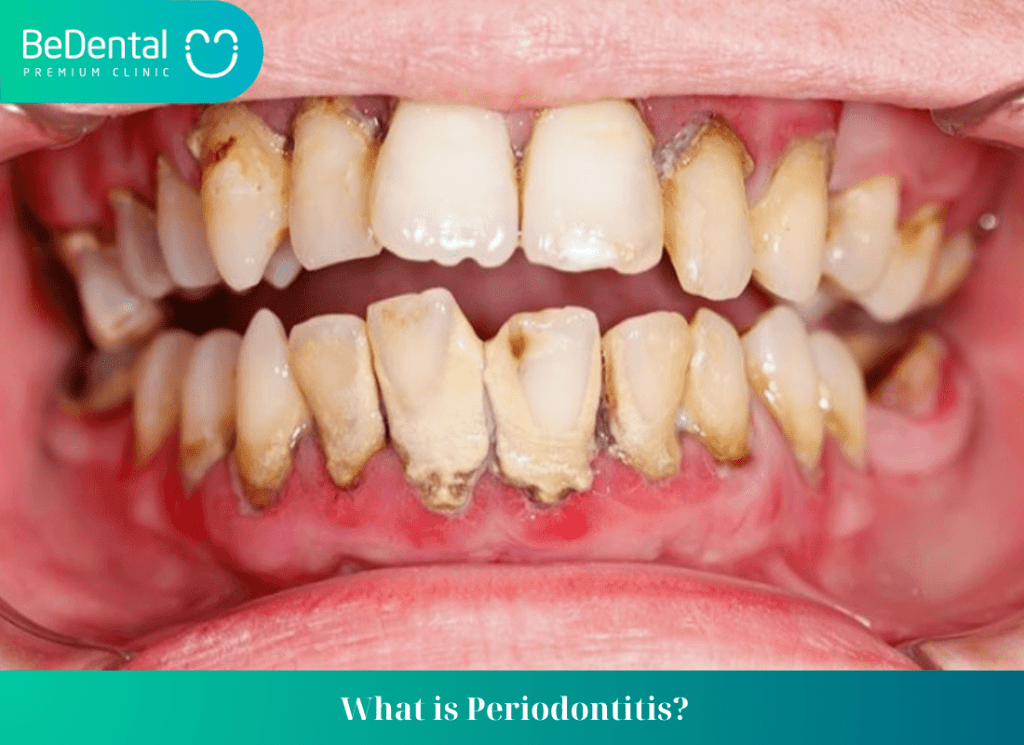
Gum inflammation only affects the tissues around the teeth and commonly occurs in cases of adolescents and older adults.
Causes of Periodontitis, gingivitis
Plaque
In most cases, Periodontitis begins with plaque – a sticky film on the teeth primarily composed of bacteria. If not treated, the teeth can develop Periodontitis:
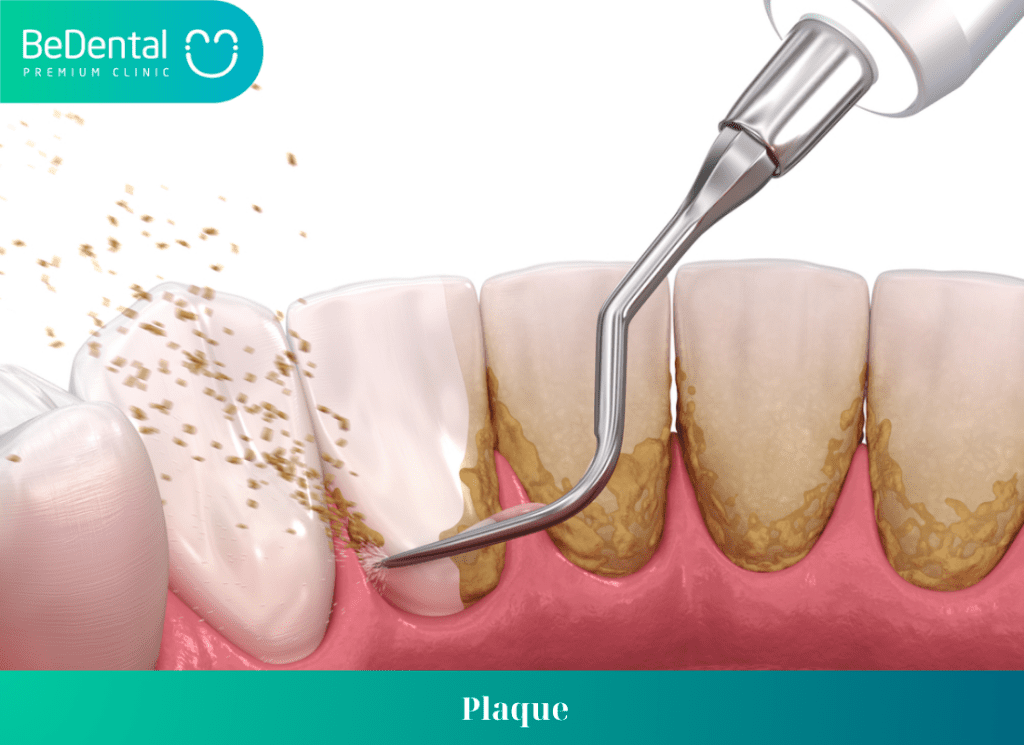
- Plaque on the teeth interacts with bacteria in the oral cavity when consuming starch and sugar. Brushing your teeth twice a day and using dental floss daily will remove plaque, but stubborn plaque will not be removed quickly.
- Plaque hardens under the gum line and, over time, turns into tartar. Tartar is more difficult to remove than plaque because it contains more bacteria. The more plaque and tartar on the teeth, the more damage they cause. Tartar cannot be removed by brushing and flossing alone; a dental visit is required to eliminate it.
- Plaque can cause gingivitis, which is the mildest form of Periodontitis. Gingivitis is characterized by swelling and inflammation of the gums around the base of the teeth. It can be fully cured when treated with the correct method, combined with good oral care at home.
See more: What is Zirconia Dental Crown?
Adolescent gingivitis
Periodontitis can initially originate from adolescent gingivitis. If not treated and addressed in a timely manner, gingivitis can negatively affect oral health. It can lead to periodontal disease and may develop into more serious complications.
Poor oral hygiene
Additionally, improper oral hygiene is another contributing factor to periodontal disease. Individuals with poor oral care habits tend to develop plaque around the base of their teeth. If this plaque is not properly removed, it creates a favorable environment for bacteria to grow and cause infections.
Other causes of periodontal disease
Aside from the aforementioned causes, periodontal disease can also result from other factors such as:
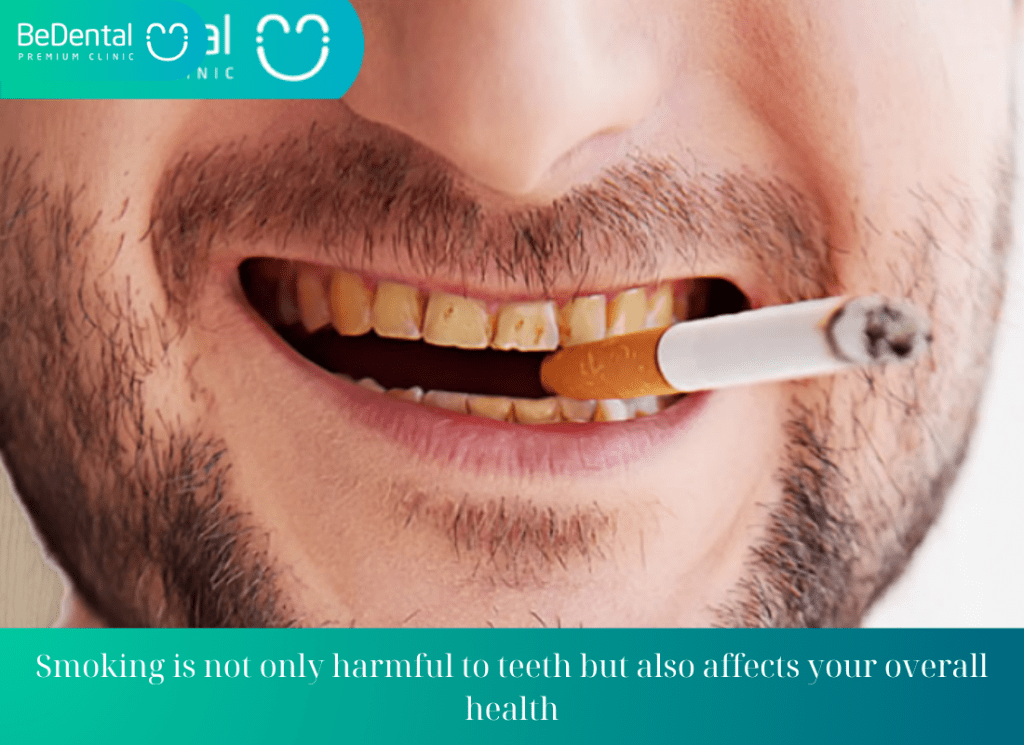
- Weak teeth in older adults.
- Smoking and substance abuse.
- Hormonal changes due to pregnancy or menopause.
- Inadequate and unscientific nutrition.
- Genetic factors.
- Use of antibiotics or dehydration-inducing medications.
- Patients with immune system disorders such as leukemia, cancer, HIV/AIDS.
- Other medical conditions such as diabetes, arthritis, obesity.
See more: Do braces hurt?
Impact of gum disease on teeth and gums
The impact of gum disease on teeth and gums can lead to serious issues and damage. Here are the main effects that gum disease can cause:
- Gum tissue loss: Gum disease causes inflammation, swelling, and bleeding of the gums. When continuously damaged, the gum tissue may recede, leading to gum tissue loss and root exposure, making the teeth more sensitive and prone to damage.
- Gum pocketing: Gum disease can lead to the formation of gum pockets, which are deep areas below the gums filled with plaque and bacteria. These pockets provide a favorable environment for bacterial growth, causing further damage to the gum tissue and jawbone.
- Tartar buildup: Gum disease is a primary cause of tartar buildup, a condition where plaque containing bacteria firmly adheres to the tooth surface. Tartar not only makes the teeth unsightly but also provides a conducive environment for bacterial growth, causing bad breath and serious damage to the gum tissue.
- Jawbone destruction: Bacteria in gum disease can invade the jawbone and cause bone destruction. If not treated promptly, this condition can lead to jawbone loss and affect the structure and stability of the teeth.
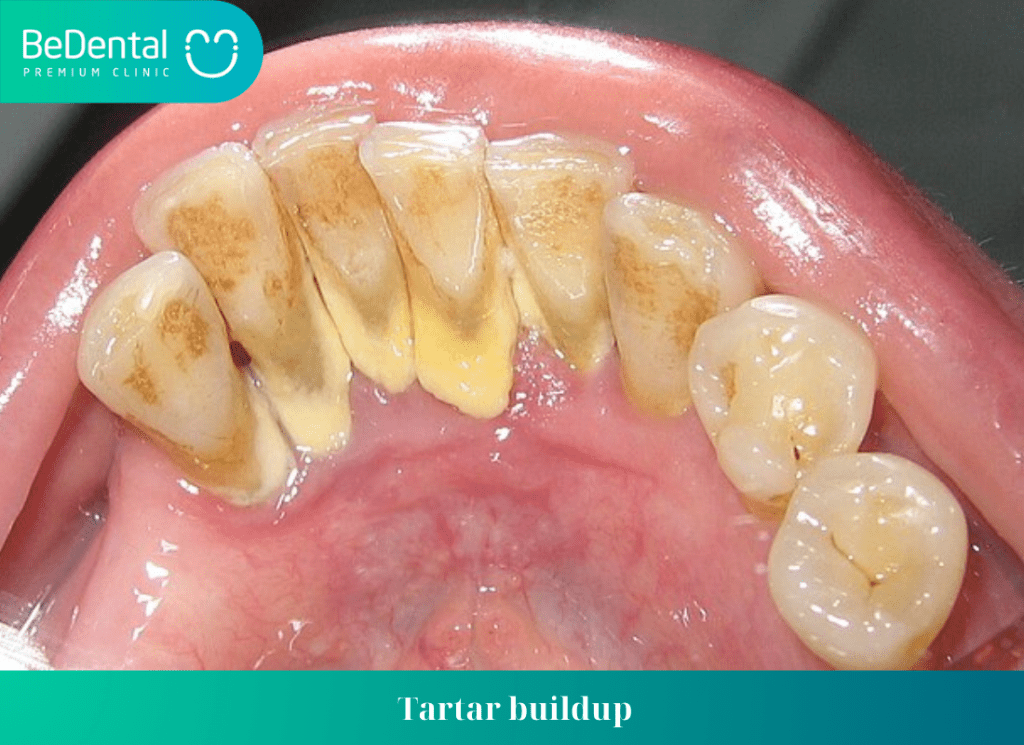
- Tooth loss: Periodontitis is the primary cause of tooth loss in adults. Bacteria and plaque cause destruction of the tissue surrounding the teeth, making the teeth lose support and eventually fall out.
4 stages of Periodontitis development
Here are the 4 stages of Periodontitis development that you should not overlook. These 4 stages range from mild to severe, and if ignored, can lead to a more serious progression of the disease.
- Stage 1: Tooth calcification, high teeth formation leading to the formation of yellow plaque deposits on the teeth.
- Stage 2: Swollen gums, especially bleeding when chewing food, brushing, or flossing.
- Stage 3: Gums with pus.
- Stage 4: Receding gums, bone destruction. More severe symptoms include loose teeth and tooth loss.
See more: What are crookd front teeth?
Diagnosis methods for Periodontitis
To determine whether a patient has Periodontitis and its severity, a dentist will perform the following diagnostic methods:
- Inquire about medical history or factors that may contribute to the appearance or worsening of symptoms such as smoking or using certain medications that cause dry mouth.
- Examine the teeth to look for plaque buildup and high teeth accumulation and assess whether bleeding is easy.
- Measure the depth of gum pockets between the gum line and teeth by placing a dental probe at the side of the tooth and under the gum line. If the gums are healthy, the pocket depth will be between 1-3 mm. If the pocket is deeper than 4 mm, it may indicate Periodontitis, and if deeper than 6 mm, it may not be completely clean.
- Dental X-rays to check for bone loss in the areas where the dentist has measured pocket depth.
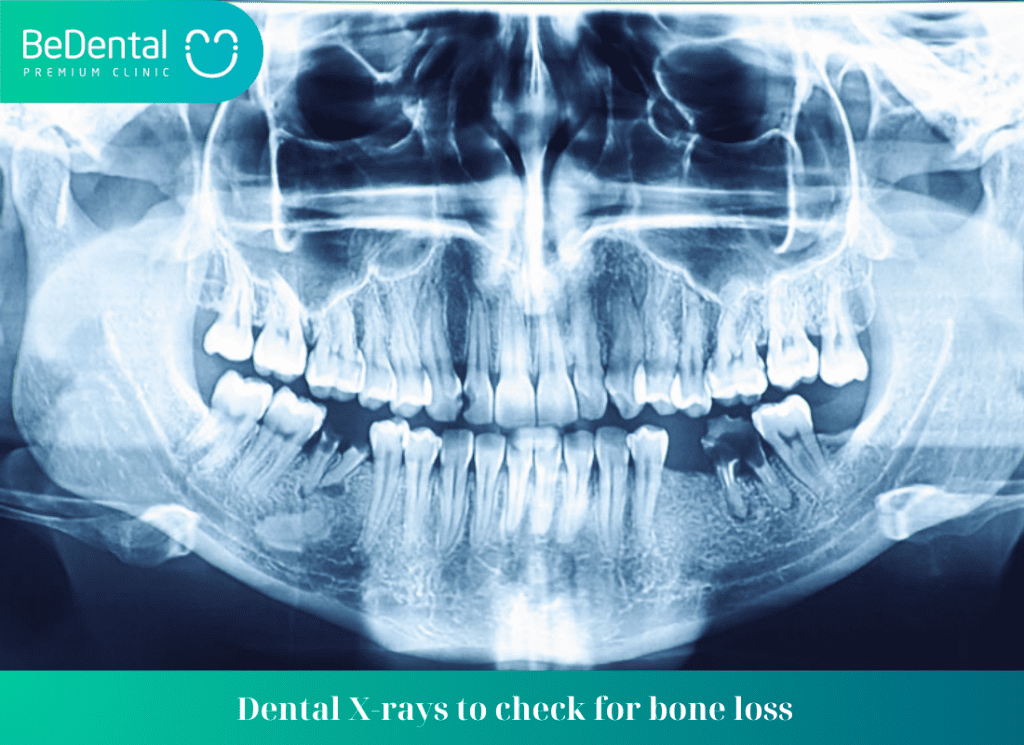
Recognizing gum disease through the following signs
Gum disease is easily detected based on the following characteristics:
- Early warning signs of gum disease include: tooth calcification, high teeth forming plaque at the base of the teeth. Gums are swollen and bleeding occurs when chewing, brushing, or flossing.
- More severe signs include pus from the gums, bad breath, loose teeth, and teeth spacing due to shifting.
Treatment of gum disease
How is gum disease treated? Depending on the severity of gum disease, dentists will choose appropriate treatment methods.
See more: What is a misaligned bite?
Emergency treatment with antibiotics
This is a temporary treatment method when the gum area is swollen and the mucous membrane is inflamed. Antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs are commonly used for treatment. However, this is only a temporary solution as the disease can develop into chronic and recurrent.
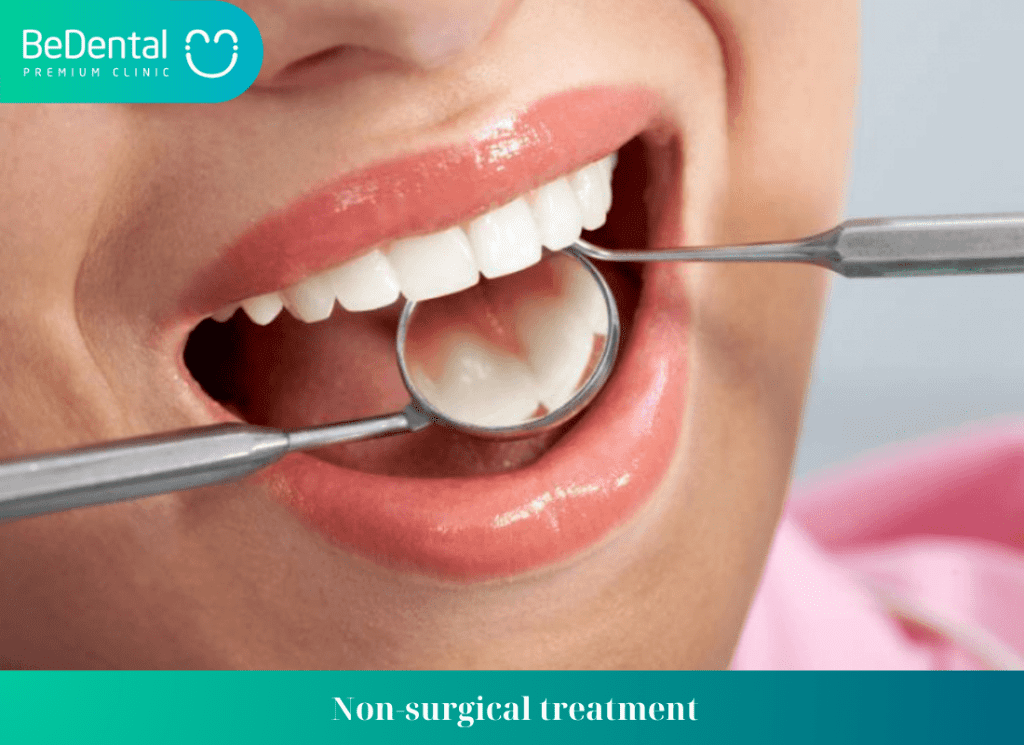
Non-surgical treatment
For mild gum disease, doctors will treat using non-surgical methods. Doctors will apply anti-inflammatory and antiseptic medications to the gum area. Then, plaque will be removed, loose teeth will be stabilized, or teeth may be extracted if they cannot be saved.
Surgical treatment
This method is only applied when other treatments are ineffective. Common surgical methods used by dentists include: gum pocket surgery, regeneration surgery, soft tissue grafting surgery, etc.
Guidelines on how to prevent Periodontitis
Preventing Periodontitis is an important part of maintaining oral health. Here are some suggestions on how to properly care for your teeth to reduce the risk of Periodontitis:
- Brushing technique: Brush your teeth at least twice a day for at least two minutes each time. Use a soft toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste to remove plaque and bacteria.
- Use dental floss and an interdental brush: Use dental floss and an interdental brush daily to clean areas that the toothbrush cannot reach, such as between teeth and along the gumline.
- Use antibacterial mouthwash: Use mouthwash containing antibacterial properties to eliminate bacteria and reduce inflammation in the mouth.
- Limit exposure to irritants: Avoid smoking and using electronic cigarettes. Also, limit exposure to other irritants like alcohol and caffeine.
- Limit sugar consumption: Sugar is a food source for bacteria in the mouth. Limiting sugar intake and other sweet products can help reduce the risk of Periodontitis.
- Treat oral problems promptly: Treat oral issues such as plaque buildup, cavities, and gum infections promptly to prevent the development of Periodontitis.
- Regular dental check-ups: Schedule regular dental check-ups to examine and clean your teeth. Dental professionals can detect and treat issues related to Periodontitis early.
See more: How to attach gems to teeth?
Customers showing signs or currently suffering from Periodontitis should visit BeDental for examination and treatment using appropriate methods!
Conclusion
In conclusion, Periodontitis is a common oral health issue that can lead to serious consequences if left untreated. Recognizing the signs of Periodontitis, such as tooth calcification, swollen gums, and loose teeth, is crucial for early intervention and effective treatment.
Diagnosis methods, including dental examinations and X-rays, help dentists determine the severity of the disease and choose appropriate treatment options. From emergency antibiotic treatment to non-surgical and surgical interventions, there are various ways to address Periodontitis based on its progression.
Preventing Periodontitis through proper oral care practices, such as brushing technique, flossing, using mouthwash, limiting exposure to irritants, and maintaining regular dental check-ups, is essential for maintaining oral health and reducing the risk of developing Periodontitis.
By following these preventive measures and seeking timely treatment for oral issues, individuals can protect their gums and teeth from the harmful effects of Periodontitis. Remember, early detection and proactive care are key to preventing and managing Periodontitis effectively.
Leave your information if you would like further dental consultation.
Tư vấn chuyên môn bài viết:
BÁC SĨ DƯƠNG THỊ THÙY NGA
BEDENTAL - TOP STANDARD DENTISTRY SYSTEM
In HANOI
Address 1: 7B Thi Sach St, Ngo Thi Nham, Hai Ba Trung Dist, Ha Noi. - 0934.61.9090
Address 2: No 129 Hoang Ngan, Yen Hoa, Cau Giay Dist, Ha Noi. - 0934.61.9090
In HO CHI MINH
Address 1: 53 -55 -57 Pho Duc Chinh St, Nguyen Thai Binh, Dist. 1, Ho Chi Minh. - 0766.00.8080
Working: 9am - 8pm everyday
Website: https://bedental.vn/en/

 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt 한국어
한국어 日本語
日本語 中文 (中国)
中文 (中国)