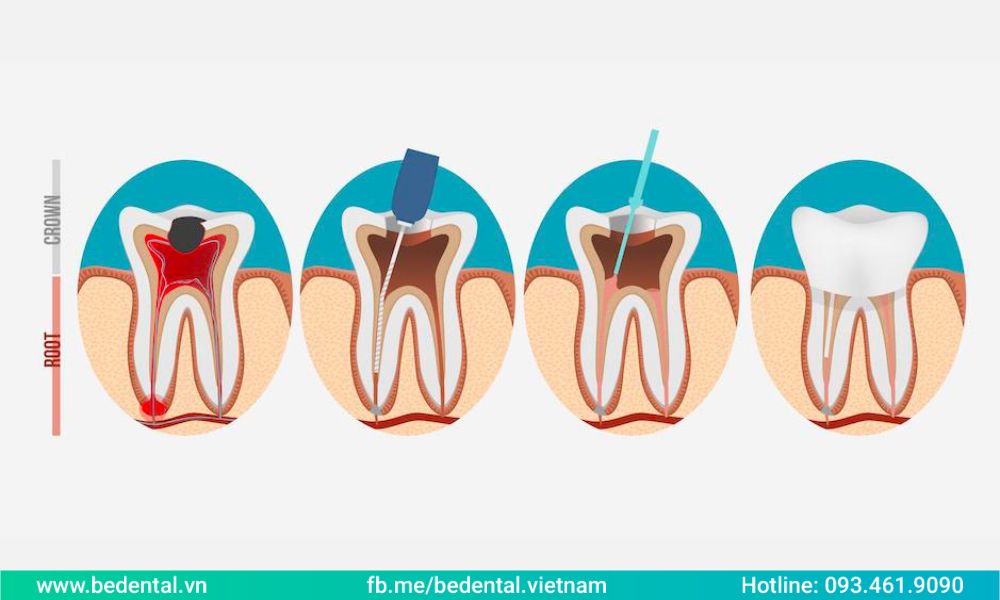
In order to fill the hole on the tooth where the decaying material was removed, your dentist will first eliminate the damaged segment of the tooth.
Furthermore, tooth fillings are made to restore teeth that have been worn down, including cracked or fractured teeth (such as from nail-biting or tooth grinding).
Tooth Fillings Procedure
The tooth’s surrounding tissue will first be temporarily numb by the dentist using a local anesthetic. Next, the decayed portion will be removed using a drill, air abrasion tool, or laser. The dentist’s comfort level, training, and investment in the specific piece of equipment, as well as the site and extent of the decay, all have an impact on the tool choice.
To confirm if all of the decay has been removed, your dentist will then probe or test the spot. As soon as the decay is completely eliminated, the dentist will prepare the gap for the filling by clearing the cavity of bacteria and debris.
If the decay has already extended near the root, your dentist has to put in a liner made of glass ionomer, composite resin, or other material to protect the nerve. After placing the tooth fillings, your dentist will often polish and complete it.
For tooth fillings that fit your teeth, the following extra steps are required. Your dentist will remove the decay and clean the area before gradually applying the tooth-colored material. Then a certain light is used to “cure” or harden each layer. After completing the multilayering process, the dentist will shape the composite material to get the desired result, trim off any excess material, and polish the final repair.
Types of Tooth Fillings Materials
There are several dental filling materials available today. Gold, porcelain, silver amalgam (mercury combined with silver, tin, zinc, and copper), tooth-colored plastic, and substances known as composite resin fillings are all options for filling teeth. Another substance, called as glass ionomer, also includes glass particles. Similar to how composite resin fillings are used, this substance is utilized.
Depending on the location and extent of the decay, the cost of the material, your insurance coverage, and their recommendations, the type of filling that is best for you will vary.
Cast Gold Fillings
Advantages of cast gold fillings:
- Durability: lasts at least ten to fifteen years, and frequently much longer; doesn’t corrode a strong jaw that can sustain chewing pressure
- Aesthetics: Compared to silver amalgam fillings, some patients feel gold to be more aesthetically beautiful.
Cast-gold fillings’ drawbacks:
- Cost: Gold cast fillings are up to 10 times more expensive than silver amalgam fillings and more expensive than other materials.
- Additional office appointments: at least two office visits are necessary to put
Filled with silver (Amalgams)
Benefits of having silver fillings:
- Durability: Silver fillings often outlive composite (tooth-colored) fillings by at least 10 to 15 years.
a strong jaw that can sustain chewing pressure - Cost: may be less costly than composite fillings
Disadvantages of silver fillings:
- Poor aesthetics: Silver tooth fillings are unattractive because they don’t match the color of natural teeth. More tooth structure is lost since it’s frequently necessary to remove good tooth tissue to create a cavity big enough to fit the amalgam tooth filling.
- Discoloration: Amalgam tooth fillings can give the tooth structure around them a gray appearance.
- Cracks and fractures: All teeth expand and contract in the presence of hot and cold liquids, which can ultimately result in the tooth cracking or breaking. However, amalgam material, when compared to other filling materials, may experience a wider degree of expansion and contraction, which may result in a higher incidence of cracks and fractures.
- Allergic reactions: Around 1% of the population has a sensitivity to the mercury used in amalgam tooth fillings.
Low quantities of mercury are released from the amalgam in the form of a vapor that may be breathed and absorbed by the lungs. Exposure to mercury vapor at high levels is linked to negative effects on the kidneys and the brain. The FDA deems amalgam tooth fillings safe for adults and kids aged 6 and older since studies have not connected them to health issues.
Tooth-colored Composites
Advantages of composites:
- Aesthetics: Composite tooth fillings can be accurately matched in tone and color to surrounding teeth. Front teeth or other visible areas of teeth are particularly well suited for usage with composites.
- Bonding to tooth structure: Composite fillings micro mechanically attach to tooth structure to provide further support.
- Versatility: Composite fillings can be used to repair chipped, cracked, or damaged teeth in addition to serving as a decay-filling substance.
- Tooth-sparing preparation: When eliminating cavities and preparing for the filling, less tooth structure may need to be removed than when using amalgam fillings.
Disadvantages of composites:
- Lack of durability: These tooth fillings are often composed of porcelain and are more stain-resistant than materials made of composite resin. This substance may cost as much as gold and often lasts for more than 15 years.
- Increased chair time: Due to the method used to apply the composite material, these tooth fillings might take up to 20 minutes longer to place than amalgam fillings.
- Additional visits: More than one office visit may be necessary if composites are utilized for inlays or onlays. Depending on the placement, composite materials have the potential to chip away at the tooth.
- Cost: Composite fillings can be up to twice as expensive as amalgam ones.
There are two more tooth-colored fillings besides tooth-colored composite resin fillings: ceramics and glass ionomer.
Other Filling Types
Ceramics. These tooth fillings are often composed of porcelain and are more stain-resistant than materials made of composite resin. This substance may cost as much as gold and often lasts for more than 15 years.
Acrylic and a certain kind of glass are used to create glass ionomers. This substance is most frequently utilized for fillings in young children and below the gum line (drilling is still required). Fluoride is released by glass ionomers, which can aid in preventing additional tooth decay. Though less durable than composite resin, this substance is more brittle and prone to wear. Glass ionomer typically has a lifespan of five years or fewer and costs about the same as composite resin.